AI powers discovery of new CBLB inhibitor ISM3830
Posted: 2 December 2025 | Drug Target Review | No comments yet
Insilico Medicine has announced ISM3830, an AI-designed CBLB inhibitor that has demonstrated promising preclinical results.


Insilico Medicine, a clinical-stage company specialising in generative AI for drug discovery, has announced the development of a new AI-designed cancer immunotherapy candidate, ISM3830. Designed by the company’s proprietary AI platform, the compound targets Casitas B-lineage lymphoma-b (CBLB), an intracellular checkpoint and key negative regulator of T-cell and natural killer (NK) cell activation. By inhibiting CBLB, ISM3830 has shown strong potential to modulate immune tolerance and enhance T-cell and NK-cell activity, including restoring function in exhausted T cells.
Research to date indicates that CBLB is highly expressed across multiple immune cell subsets and in a wide range of cancers. These findings make CBLB an extremely promising immunotherapy target with strong clinical potential.
AI-driven discovery
Insilico describes ISM3830 as a potential best-in-class, orally available and highly selective CBLB inhibitor built on a novel scaffold generated using its proprietary AI platform.
Automation now plays a central role in discovery. From self-driving laboratories to real-time bioprocessing
This report explores how data-driven systems improve reproducibility, speed decisions and make scale achievable across research and development.
Inside the report:
- Advance discovery through miniaturised, high-throughput and animal-free systems
- Integrate AI, robotics and analytics to speed decision-making
- Streamline cell therapy and bioprocess QC for scale and compliance
- And more!
This report unlocks perspectives that show how automation is changing the scale and quality of discovery. The result is faster insight, stronger data and better science – access your free copy today
With repeated real-world proof including preclinical candidate nomination and positive clinical results, we are growing even more confident in generative AI’s potential to accelerate drug development.
“With repeated real-world proof including preclinical candidate nomination and positive clinical results, we are growing even more confident in generative AI’s potential to accelerate drug development and enable true therapeutic innovation,” said Dr Feng Ren, co-CEO and CSO of Insilico Medicine. “Equally important, CBLB inhibition, from its fundamental mechanism of action, supports indications with low response or resistance to current immune checkpoint inhibitors – an area of significant unmet need that we are determined to address with the combined force of AI speed and human intelligence.”
The novel scaffold used in ISM3830 was identified using Chemistry42 and its ADMET predictor module. More than 40 generative AI models were deployed to design candidate compounds informed by existing cocrystal structures. These candidates were iteratively evaluated and then optimised through built-in reward pipelines, followed by synthesis and comprehensive bioassays.
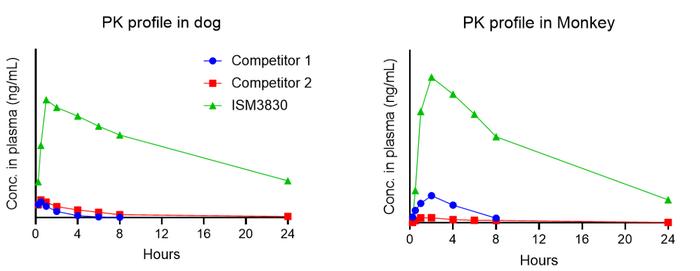

Empowered by Insilico’s proprietary generative AI platform, the drug candidate overcomes the current bottlenecks of CBLB inhibition therapies in metabolism and absorption. Preclinical safety screening demonstrated low risk of hypotension, gastrointestinal toxicity and off-target toxicity, as well as excellent selectivity and improved safety margin in DRF study. Promising druggability and excellent ADME/PK profile both in vitro and in vivo, measured by lower in vivo clearance, and higher oral bioavailability across preclinical species. Credit: Insilico Medicine
Preclinical advantages and efficacy
ISM3830 demonstrated several advantages over existing approaches to CBLB inhibition, particularly regarding metabolism and absorption – areas that have hindered development efforts previously.
ISM3830 demonstrated several advantages over existing approaches to CBLB inhibition, particularly regarding metabolism and absorption.
Preclinical safety assessments identified low risks of hypotension, gastrointestinal toxicity and off-target toxicity. The compound also showed excellent selectivity and an improved safety margin in dose-range finding studies. According to the company, ISM3830 exhibits strong druggability and favourable ADME/PK characteristics both in vitro and in vivo, including lower clearance and higher oral bioavailability across species.
In mouse models, preclinical studies revealed robust anti-tumour efficacy and evidence of long-term tumour immunity in CT26 rechallenge experiments. The candidate also showed potential for combination use with a variety of therapies, including checkpoint inhibitors, chemotherapies and targeted agents.
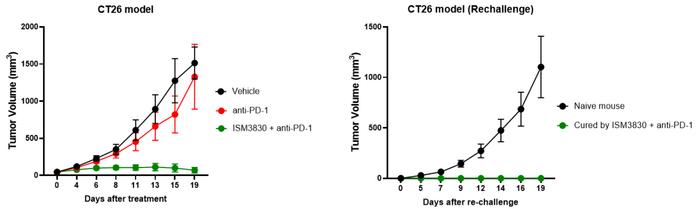

Preclinical studies suggest robust in vivo efficacy in mice models and induction of long-term tumor immunity, verified by CT26 rechallenge experiments. Additionally, combination potential was with a broad spectrum of treatment options, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, chemotherapies, and other targeted agents. Credit: Insilico Medicine.
Expanding AI-enabled drug discovery
Alongside this latest nomination, Insilico’s R&D team recently detailed the development of a related CBLB inhibitor series, outlining how structural analysis, iterative SAR optimisation and AI-guided generation informed compound evolution.
The company has also published a series of high-profile studies in covering AI-enabled programmes ranging from KRAS and ENPP1 inhibitors to pan-coronavirus therapeutics. In June, they also reported the first clinical proof-of-concept for an AI-discovered drug, Rentosertib (ISM001-055).
Since 2021, Insilico has nominated 23 preclinical candidates, with 10 receiving IND approval, as it advances a diversified pipeline across oncology, fibrosis, immunology, pain, obesity and metabolic disease.
Related topics
Animal Models, Artificial Intelligence, Checkpoint receptors, Drug Development, Drug Discovery Processes, Drug Targets, Immuno-oncology, In Vivo, Machine learning, Small Molecules, T cells, Translational Science
Related conditions
Cancer, metabolic disease, Obesity, pain
Related organisations
Insilico Medicine
Related people
Dr Feng Ren (co-CEO and CSO of Insilico Medicine)