Immunotherapy shows promise in treating high-grade glioma
Posted: 3 March 2016 | Victoria White | No comments yet
Combined with chemotherapy, a novel cell-based immunotherapy drastically increased the survival rates of mice afflicted with brain tumours. Almost 50% of the mice were completely cured…

Researchers from KU Leuven have shown that a next-generation cell-based immunotherapy may offer new hope in the fight against high-grade glioma.
Cell-based immunotherapy involves the injection of a therapeutic anticancer vaccine that stimulates the patient’s immune system to attack the tumour. Thus far, the results of this type of immunotherapy have been mildly promising. However, Abhishek D. Garg and Professor Patrizia Agostinis from the KU Leuven Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine have now found a novel way to produce more effective cell-based anticancer vaccines.
The researchers induced a specific type of cell death in brain cancer cells from mice. The dying cancer cells were then incubated together with dendritic cells, which play a vital role in the immune system. The researchers discovered that this type of cancer cell killing releases ‘danger signals’ that fully activate the dendritic cells.
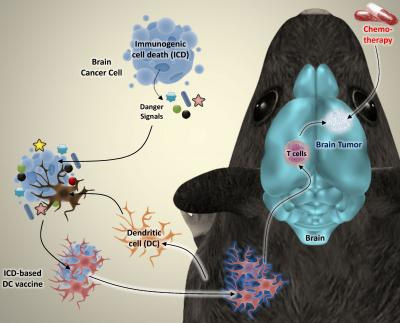

The researchers induced a specific type of cell death in brain cancer cells from mice. The dying cancer cells were then incubated together with dendritic cells, which play a vital role in the immune system. The researchers discovered that this type of cancer cell killing releases ‘danger signals’ that fully activate the dendritic cells. ©KU Leuven Laboratory of Cell Death Research & Therapy – Dr. Abhishek D. Garg
“We re-injected the activated dendritic cells into the mice as a therapeutic vaccine”, Professor Patrizia Agostinis explains. “That vaccine alerted the immune system to the presence of dangerous cancer cells in the body. As a result, the immune system could recognise them and start attacking the brain tumour.”
Almost 50% of mice were cured
Combined with chemotherapy, this novel cell-based immunotherapy drastically increased the survival rates of mice afflicted with brain tumours. Almost 50% of the mice were completely cured. For the sake of comparison: none of the mice treated with chemotherapy alone became long-term survivors.
“The major goal of any anticancer treatment is to kill all cancer cells and prevent any remaining malignant cells from growing or spreading again”, Professor Agostinis continues. “This goal, however, is rarely achieved with current chemotherapies, and many patients relapse. That’s why the co-stimulation of the immune system is so important for cancer treatments. Scientists have to look for ways to kill cancer cells in a manner that stimulates the immune system. With an eye on clinical studies, our findings offer a feasible way to improve the production of vaccines against brain tumours.”
Related topics
Immunotherapy