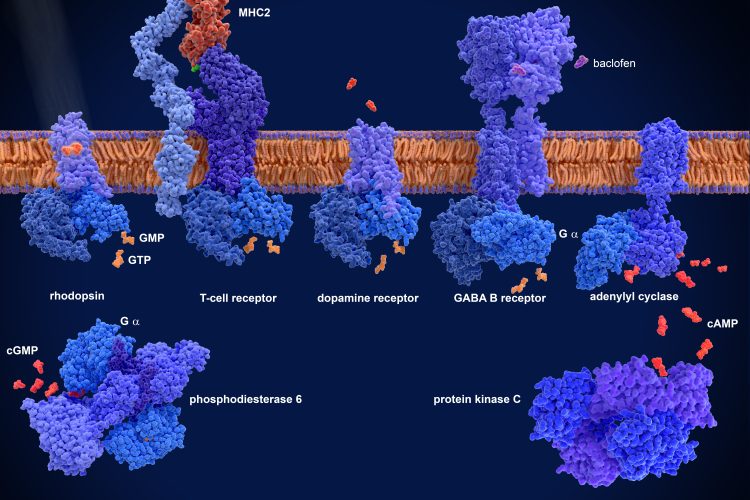
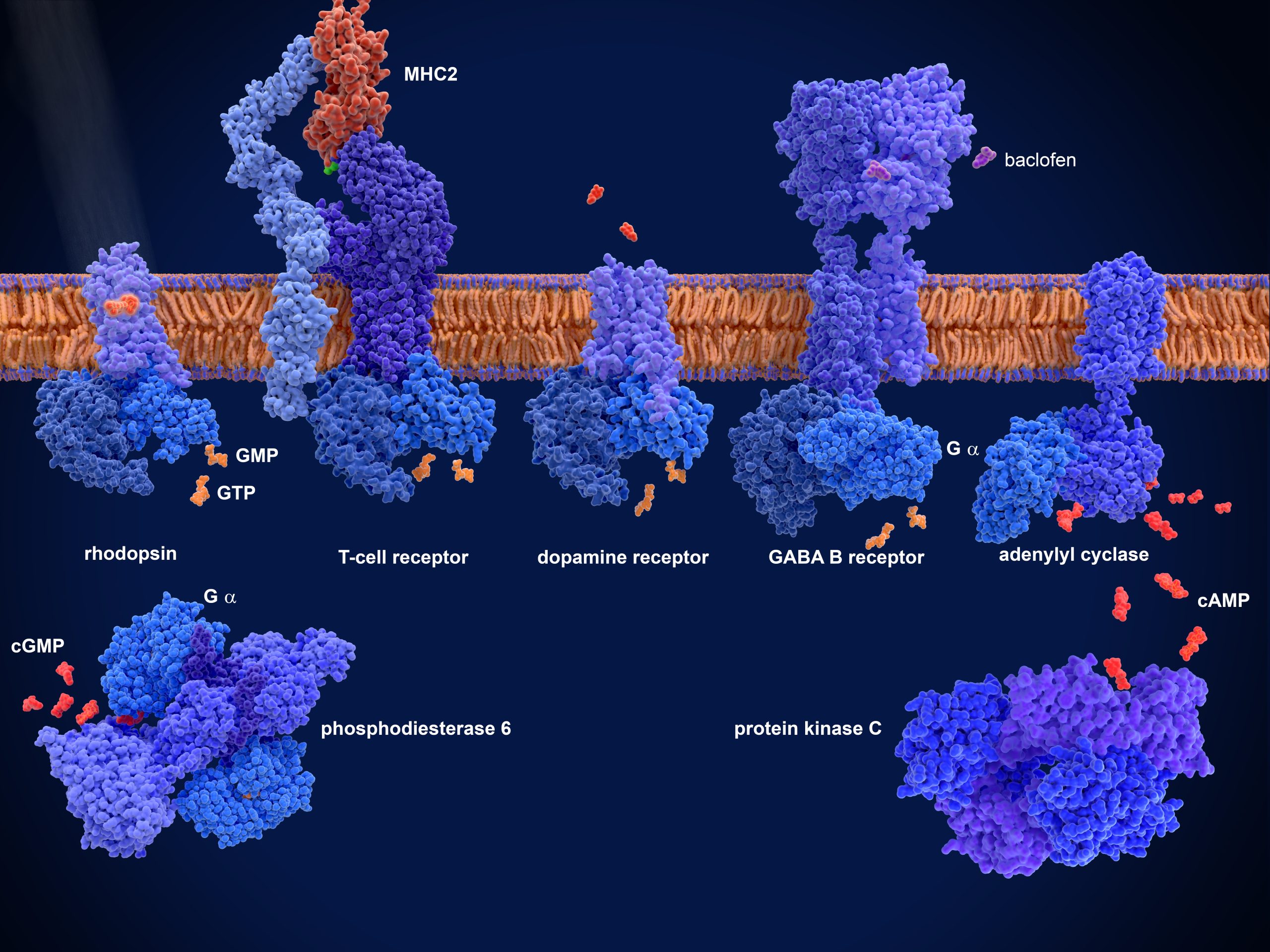
Future-proofing drug development with GenAI
Using GenAI and expert reasoning, drug developers can now explore an asset’s long-term potential as early as the preclinical stage. This shift is helping to reshape pipeline planning and refine therapeutic strategy.