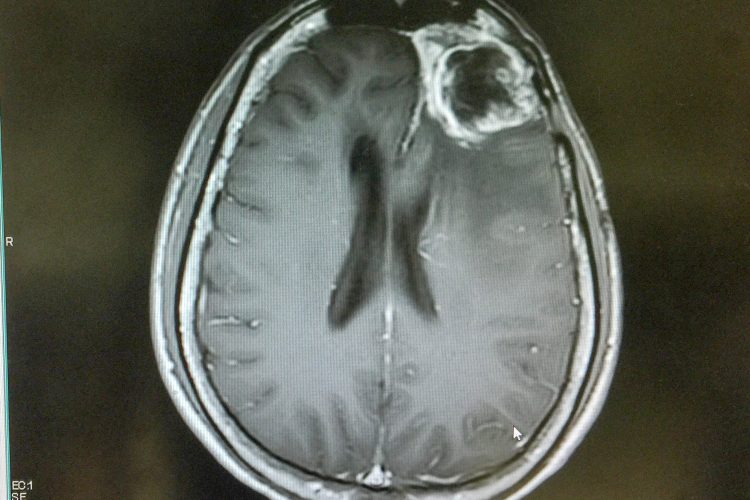
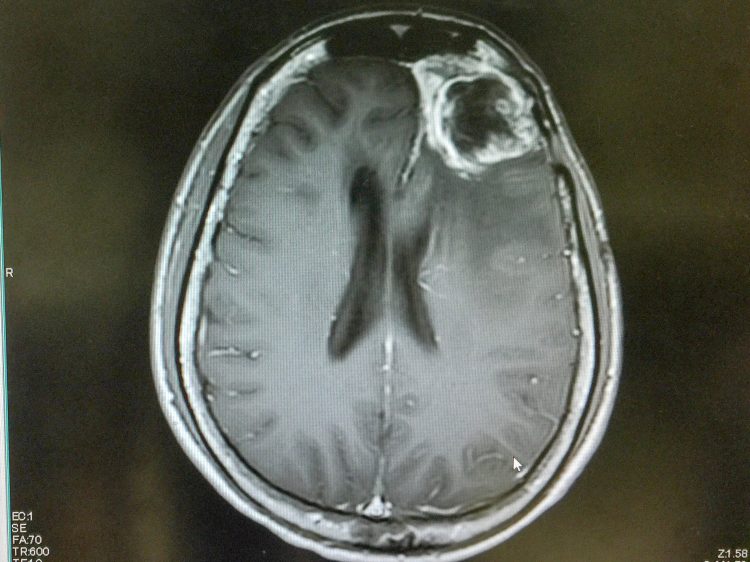
Dual CAR-T cell therapy targets T-ALL with precision
A new dual CAR-T cell therapy targeting two tumour-specific proteins in T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (T-ALL) has been developed – meaning effective treatment for this aggressive blood cancer could soon become a reality.