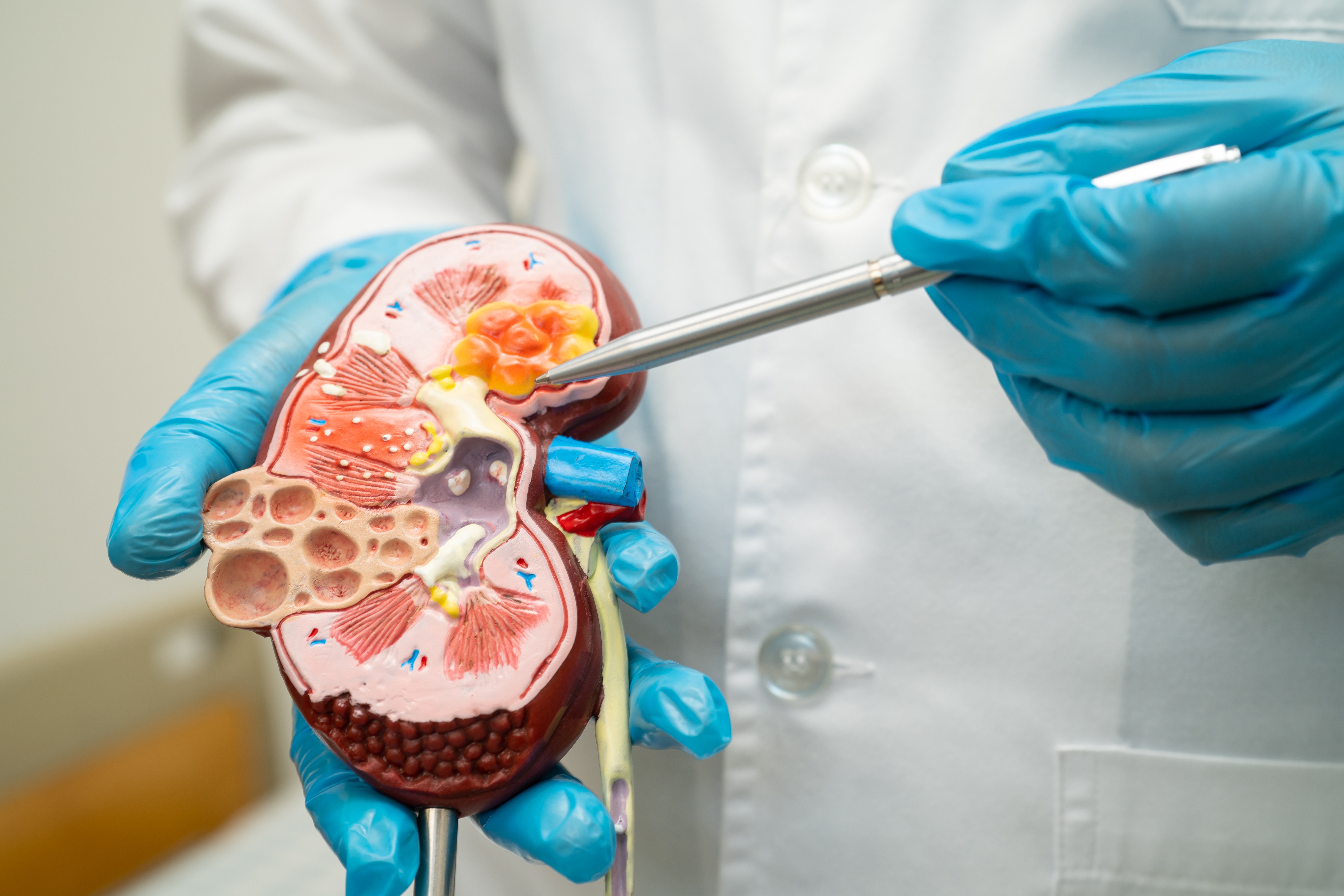
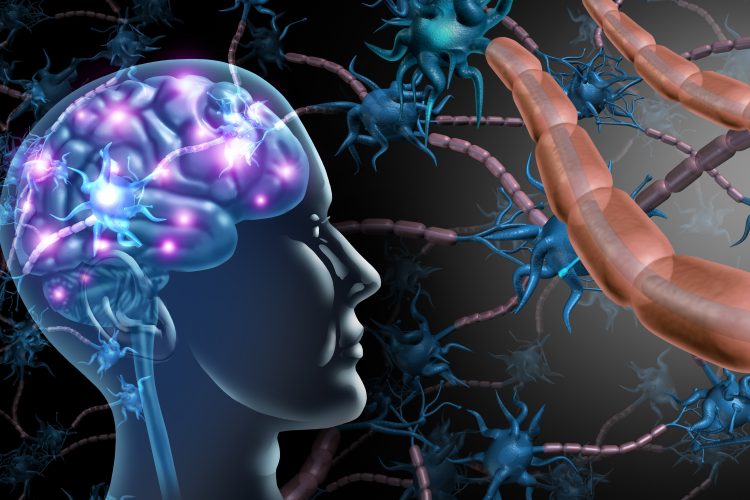
DARG cells may drive neurodegeneration in progressive MS
Scientists have discovered a rare type of brain cell that appears to drive the chronic inflammation seen in progressive multiple sclerosis – which could potentially lead to new disease-modifying therapies.