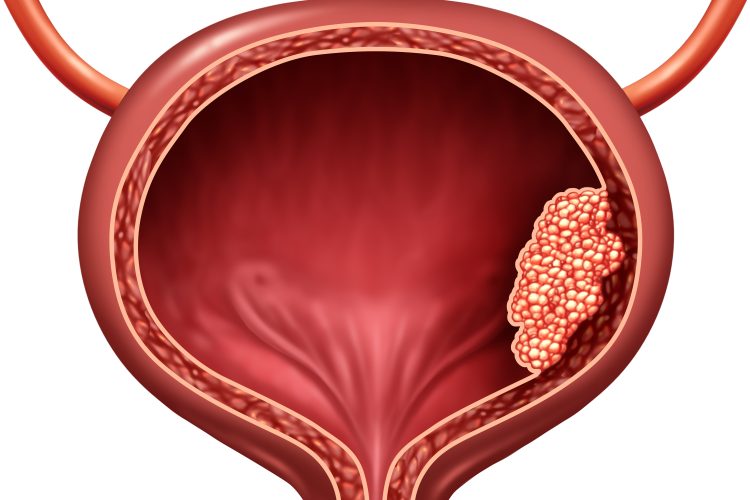
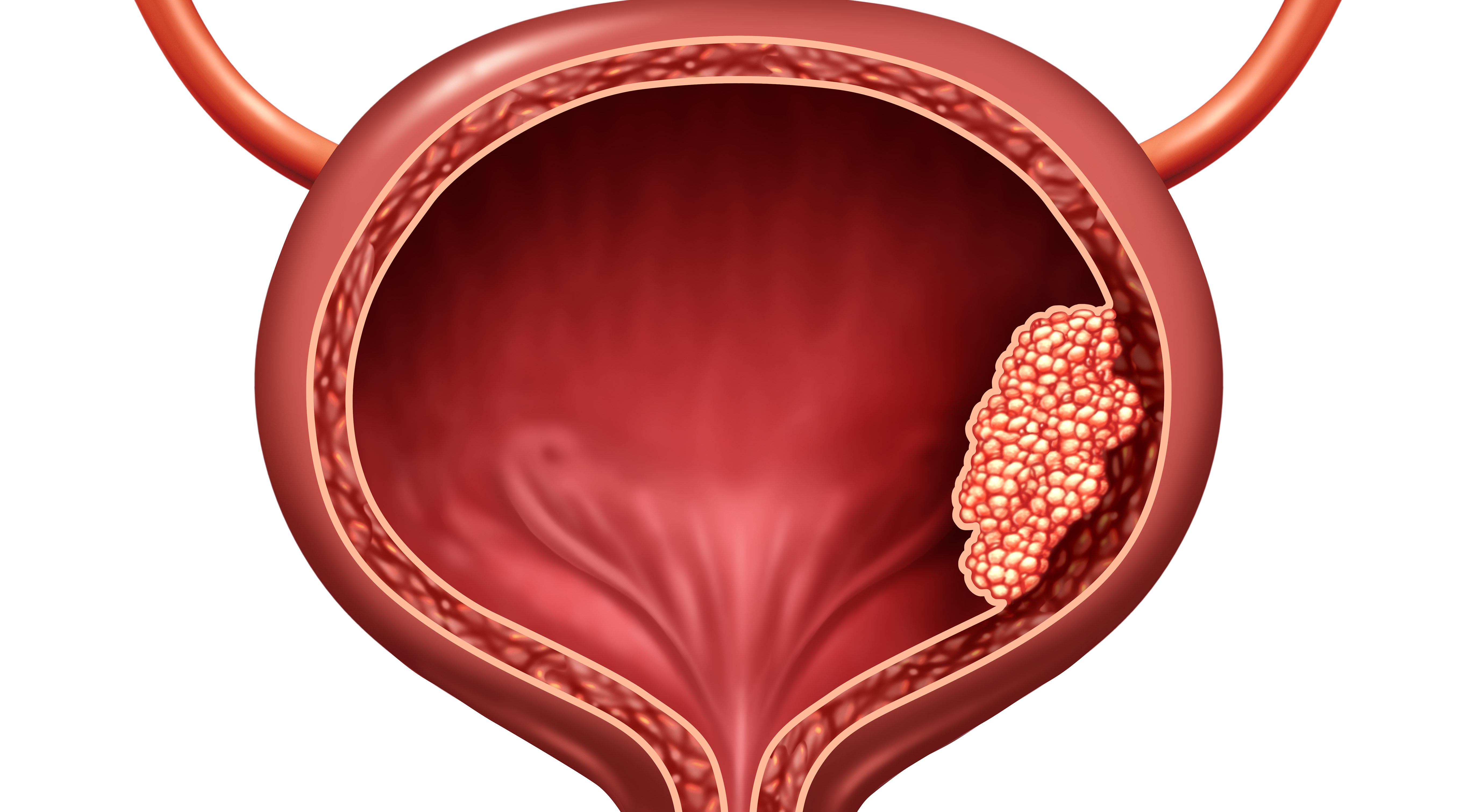
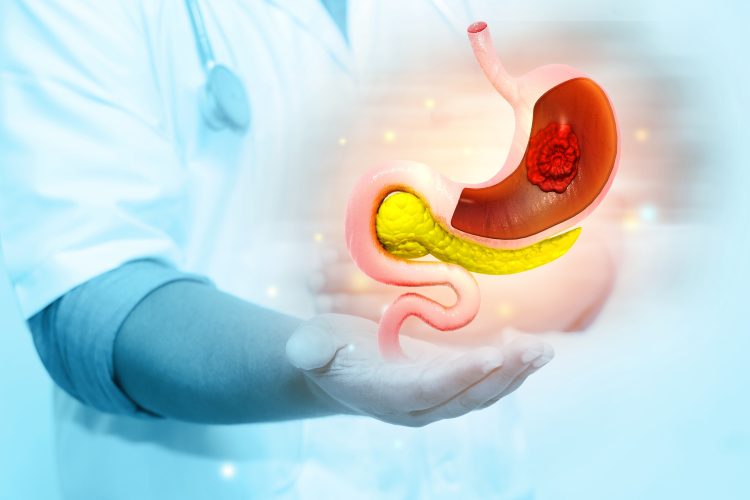
Drug trio found to block tumour resistance in pancreatic cancer models
A new study reports that a triple-targeted drug combination can drive complete and lasting regression of pancreatic tumours in preclinical models, potentially overcoming treatment resistance in one of the deadliest cancers.