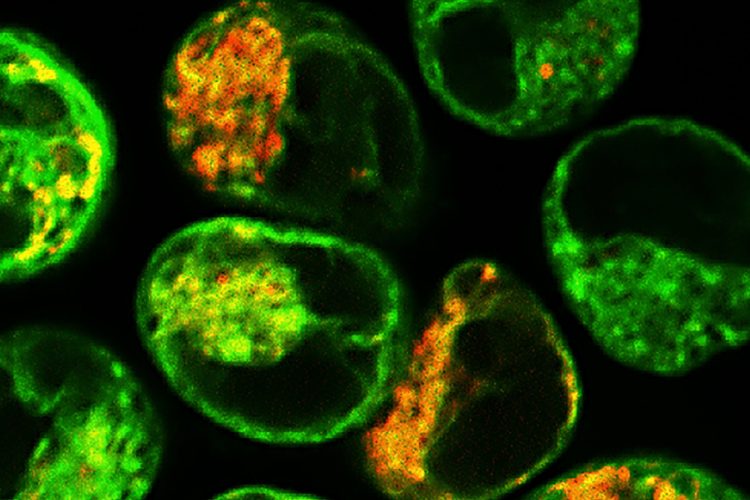
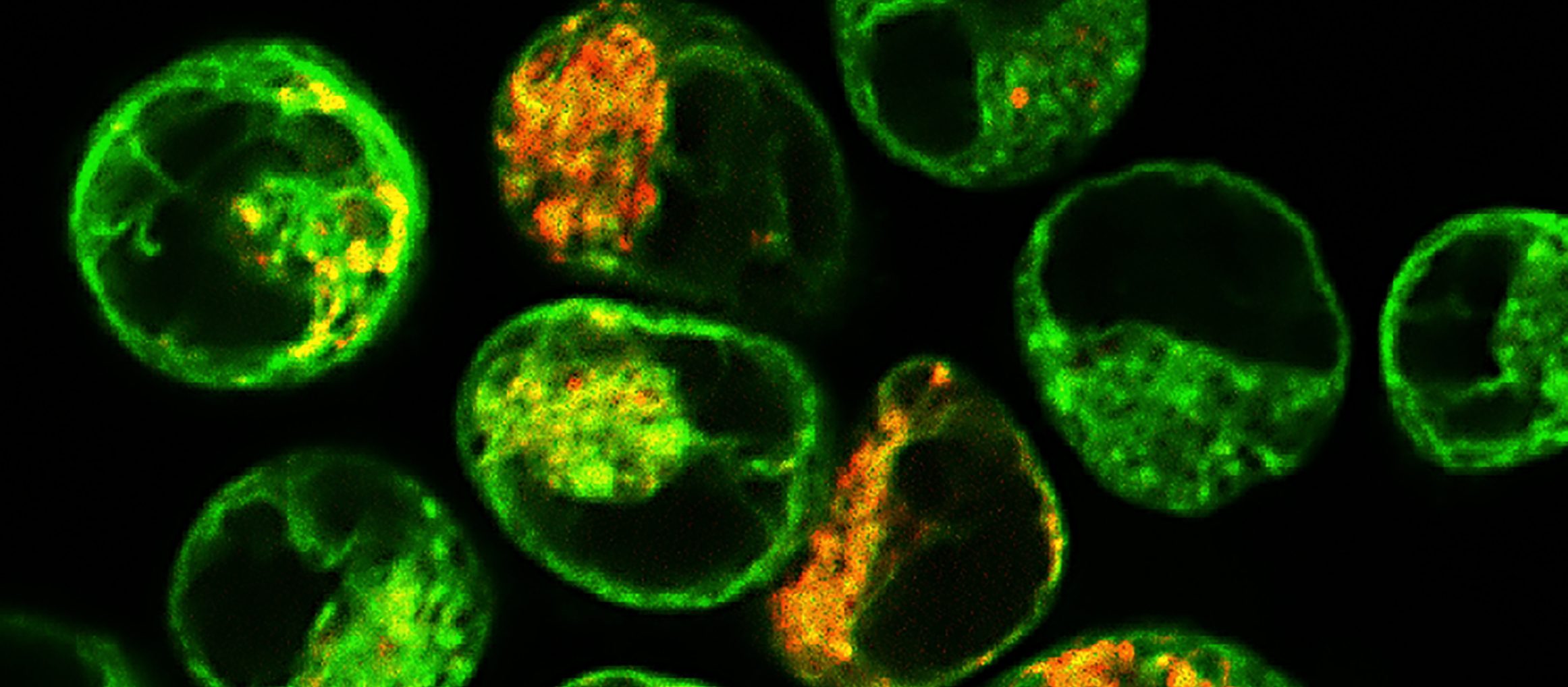
Brain discovery could improve drugs targeting amyloid diseases
New research shows the brain can intentionally form amyloids to store memories, challenging decades of thinking about neurodegenerative disease and pointing towards new strategies for drug discovery.