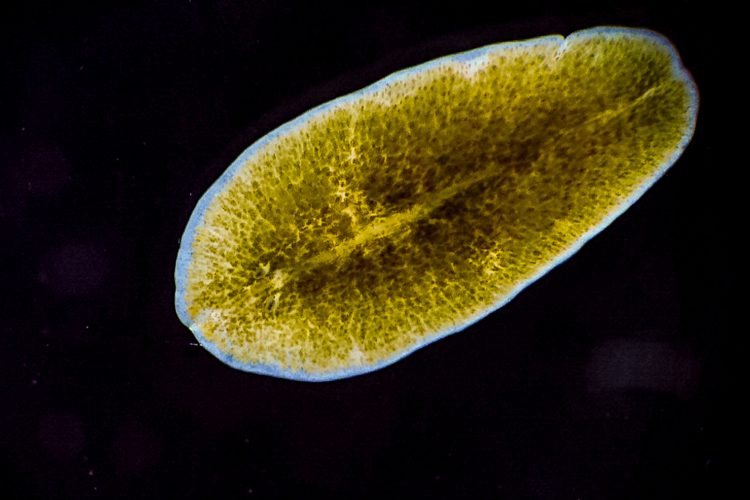
Planaria flatworms provide new way to study schizophrenia drugs
A new study has shown that small pond worms, called planaria, respond to psychiatric drugs like rodents – offering a promising new way of studying mental health conditions such as schizophrenia and addiction.