Bile acid-enhanced liver organoids set to improve liver disease treatment
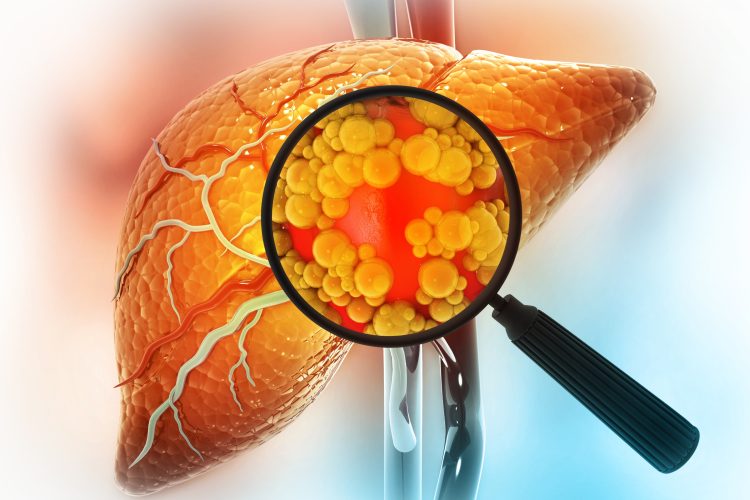
Researchers in Japan have developed long-lasting 3D liver organoids from stem cells by incorporating bile acids into the culture medium - offering a new model for studying chronic liver diseases.