SOMAscan™ assay: a vital proteomic tool in drug discovery
Posted: 21 September 2015 | SomaLogic
The SOMAscan™ assay is a highly multiplexed, sensitive, quantitative and reproducible proteomic tool for discovering biomarkers for drug discovery…
![]() Comparative interrogation of the human proteome in healthy and diseased tissues can offer deep insights into the biology of disease and lead to the discovery of new drug targets. Elucidation of protein response to drug treatment in preclinical samples can provide valuable insight into mechanism of action (MOA) and, ultimately, to biomarkers that may translate into the clinical development. Proteomic profiling in clinical samples can lead to novel, highly specific biomarkers for diagnostics and drug treatment, that are predictive, prognostic and diagnostic, enabling the realisation of personalised medicine.
Comparative interrogation of the human proteome in healthy and diseased tissues can offer deep insights into the biology of disease and lead to the discovery of new drug targets. Elucidation of protein response to drug treatment in preclinical samples can provide valuable insight into mechanism of action (MOA) and, ultimately, to biomarkers that may translate into the clinical development. Proteomic profiling in clinical samples can lead to novel, highly specific biomarkers for diagnostics and drug treatment, that are predictive, prognostic and diagnostic, enabling the realisation of personalised medicine.
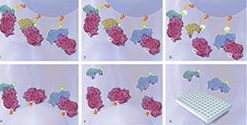
The SOMAscan™ assay is a highly multiplexed, sensitive, quantitative and reproducible proteomic tool for discovering previously undetected biomarkers for drug discovery, preclinical and clinical drug development, and clinical diagnostics, across a wide range of diseases and conditions. The SOMAscan assay measures 1,310 protein analytes in only 150μL of serum or plasma. The assay offers exceptional dynamic range, quantifying proteins that span over eight logs in abundance (from femtomolar to micromolar), with low limits of detection (38 fM median LOD in buffer) and excellent reproducibility (5.1 median %CV). The SOMAscan proteomic assay is enabled by a new generation of protein-capture SOMAmer® (Slow Off-rate Modified Aptamer) reagents. SOMAmer reagents are constructed with chemically modified nucleotides that greatly expand the physicochemical diversity of the large randomised nucleic acid libraries from which the SOMAmer reagents are selected. The SOMAscan assay measures native proteins in complex matrices by transforming each individual protein concentration into a corresponding SOMAmer reagent concentration, which is then quantified by standard DNA techniques such as microarrays or qPCR. The assay takes advantage of SOMAmer reagents’ dual nature as both protein affinity-binding reagents with defined three-dimensional structures, and unique nucleotide sequences recognisable by specific DNA hybridisation probes.
The rest of this article is restricted - login or subscribe free to access
 Thank you for visiting our website. To access this content in full you'll need to login. It's completely free to subscribe, and in less than a minute you can continue reading. If you've already subscribed, great - just login.
Thank you for visiting our website. To access this content in full you'll need to login. It's completely free to subscribe, and in less than a minute you can continue reading. If you've already subscribed, great - just login.
Why subscribe? Join our growing community of thousands of industry professionals and gain access to:
- quarterly issues in print and/or digital format
- case studies, whitepapers, webinars and industry-leading content
- breaking news and features
- our extensive online archive of thousands of articles and years of past issues
- ...And it's all free!
Click here to Subscribe today Login here
Related topics
Assays, Biomarkers, Drug Discovery, Personalised Medicine
Related organisations
SomaLogic