Studying mitosis’ structure to understand the inside of cancer cells
Posted: 19 February 2018 | Dr Zara Kassam (Drug Target Review) | No comments yet
Researchers have uncovered the architecture of the spindle pole body in yeast…
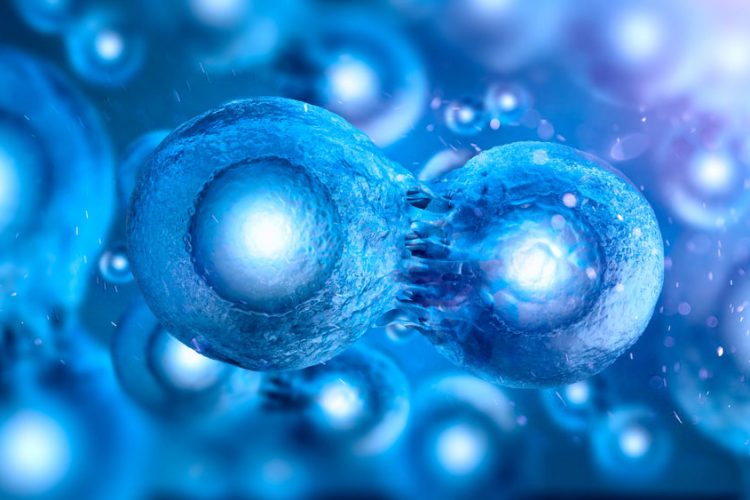


Cell division is an intricately choreographed ballet of proteins and molecules that divide the cell. During mitosis, microtubule-organising centres (MTOCs) assemble the spindle fibres that separate the copying chromosomes of DNA. While scientists are familiar with MTOCs’ existence and the role they play in cell division, their actual physical structure remains poorly understood.
Shruthi Viswanath, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, San Francisco, with a team of researchers, is trying to decipher the molecular architecture of the MTOC.
MTOCs are specially designed structures within the cell that create, anchor and stabilize the network of microtubules that act like scaffolding within the cell. More than 1,000 proteins are associated with the MTOC in animal cells, but few of these proteins have been assigned a particular function.
Biomarkers are redefining how precision therapies are discovered, validated and delivered.
This exclusive expert-led report reveals how leading teams are using biomarker science to drive faster insights, cleaner data and more targeted treatments – from discovery to diagnostics.
Inside the report:
- How leading organisations are reshaping strategy with biomarker-led approaches
- Better tools for real-time decision-making – turning complex data into faster insights
- Global standardisation and assay sensitivity – what it takes to scale across networks
Discover how biomarker science is addressing the biggest hurdles in drug discovery, translational research and precision medicine – access your free copy today
Rather than untangle the complexity of the MTOC, Viswanath focused her research on yeast cells. Within these simpler organisms, the spindle pole body (SPB) functions like the MTOC. Unlike in animal cells, the SPB of yeast contains only 18 proteins and Viswanath has initially focused on five core proteins: Spc110, Spc42, Cnm67, Spc29 and Cmd1.
Using multiple techniques such as structural modelling, X-ray scattering, X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy, Dr Viswanath and her team found that the Spc110 protein modellings a greater function in the SPB than originally believed.
At first, scientists thought these proteins acted as mere spacers holding pieces of the SPB architecture in place, but now it is believed these proteins may provide a binding surface for this architecture. This information can help understand the function of the human cell equivalent of SPBs called centrosomes. Cancer cells in most forms of cancer reveal abnormalities in the size or structure of centrosomes.
Future experiments are necessary to identify the position of other key proteins, like Spc29, a critical protein in the SPB core and to eventually identify its specific function.
Related topics
Imaging, Oncology, X-ray Crystallography
Related conditions
Cancer
Related organisations
University of California San Francisco
Related people
Shruthi Viswanath