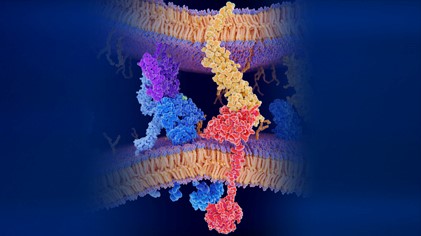
Fighting MS progression: why GPR17 is the target to watch
Despite major advances in multiple sclerosis treatment, stopping disease progression has remained out of reach. Targeting the receptor GPR17 may harness the brain’s own repair system, offering the prospect of genuine remyelination and lasting benefit for patients.