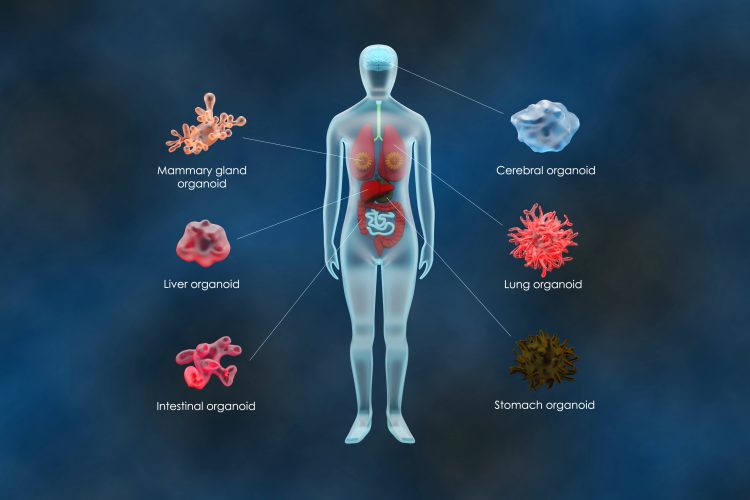
Building reliable organoid models for human-relevant drug discovery
Organoids are changing the landscape of biomedical research, with automation and AI driving new levels of consistency, scalability and human relevance. Aaron Risinger of Molecular Devices discusses how these technologies are advancing precision medicine – and the challenges that remain.