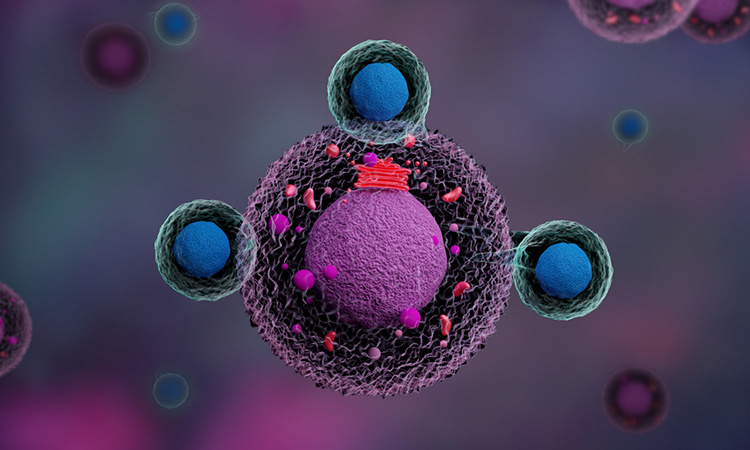
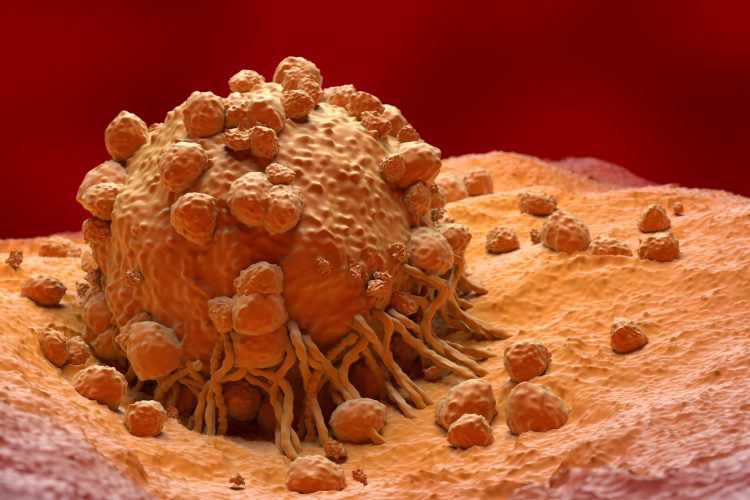
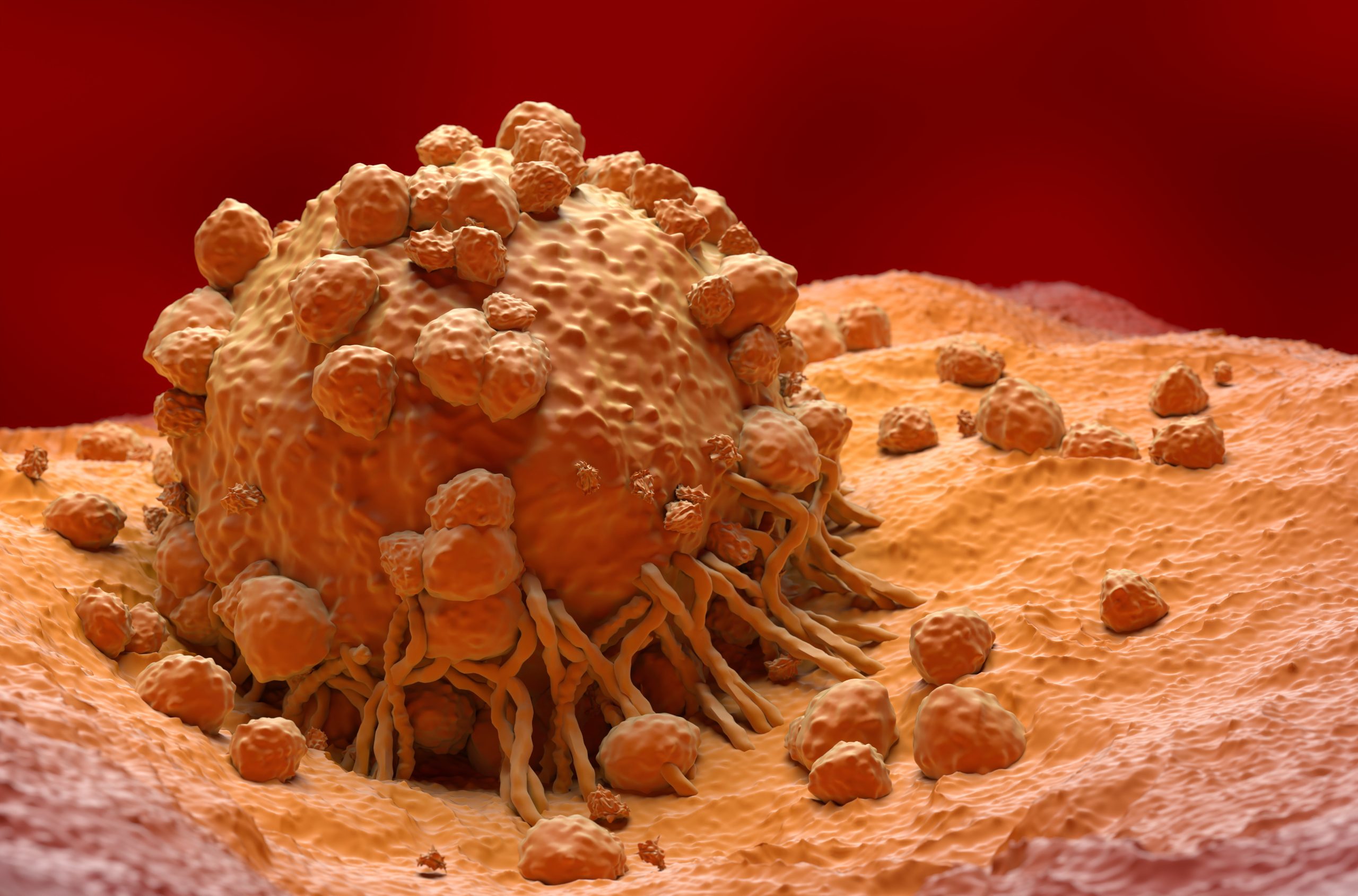
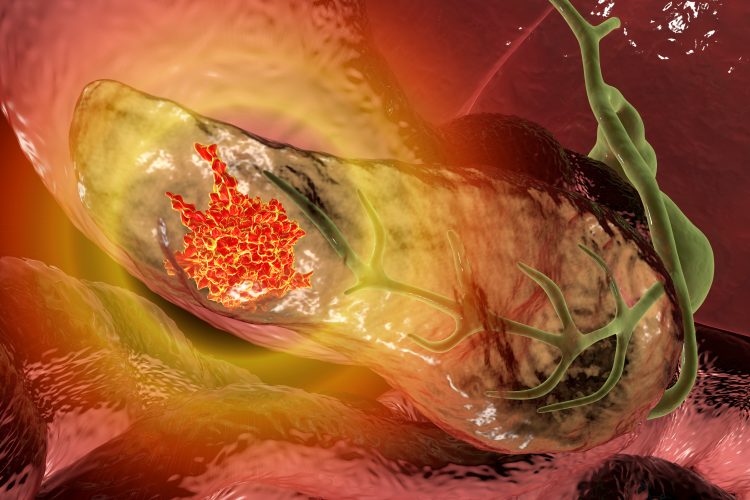
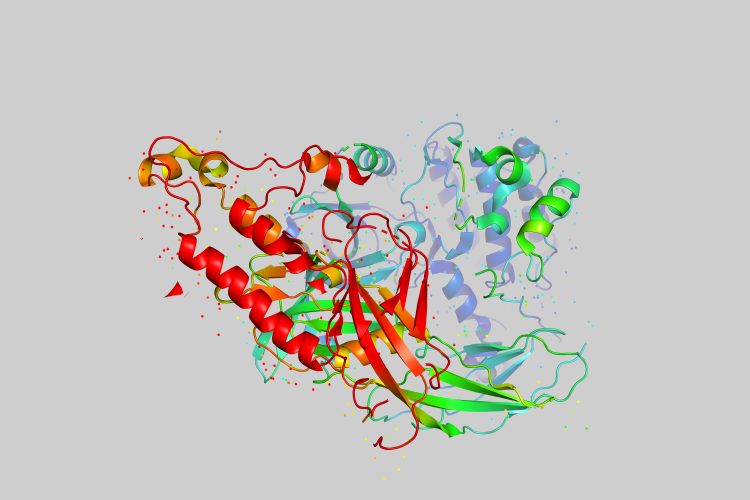
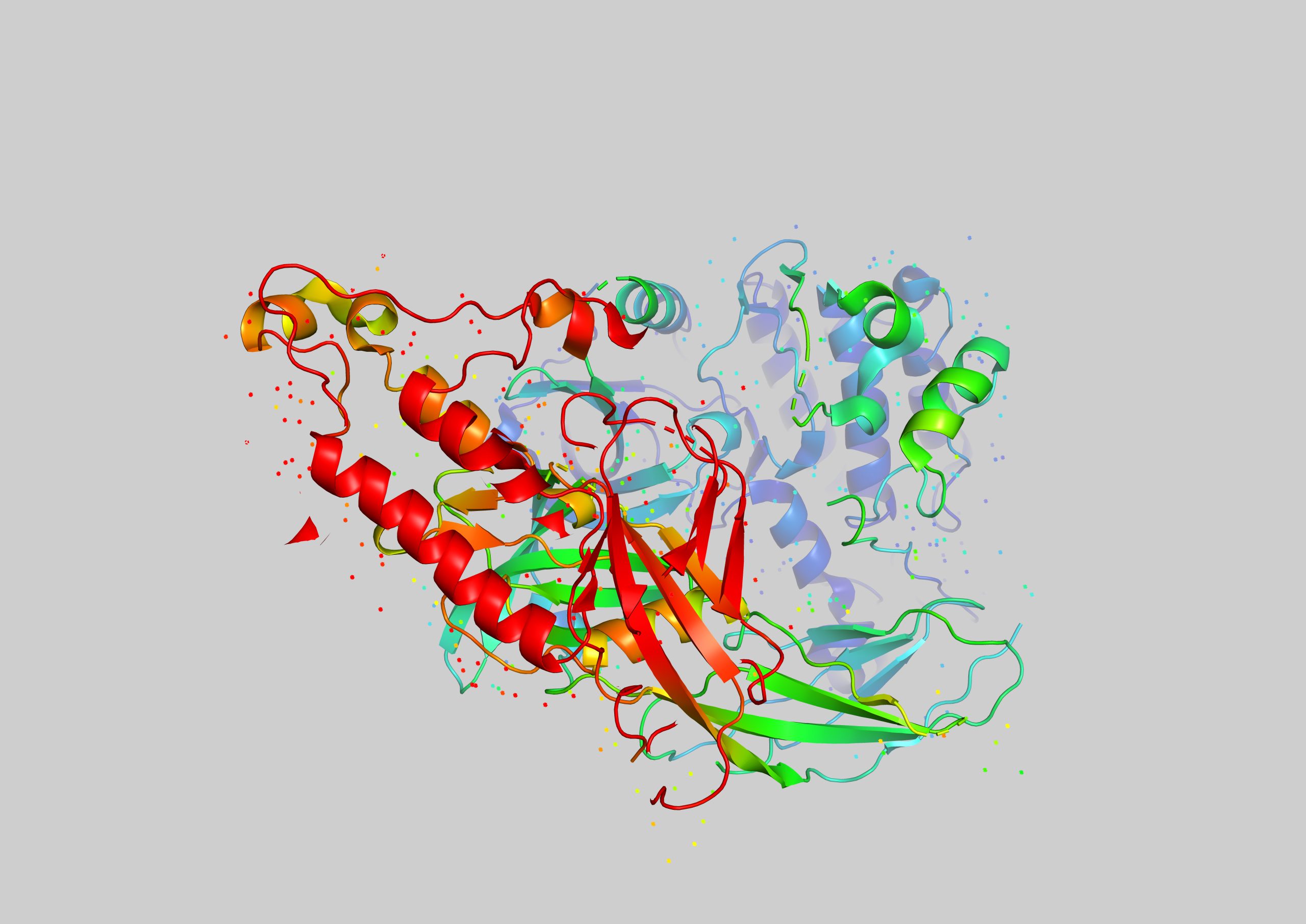
Advancing CAR-T therapy: how CD5 modulation is shaping cancer treatment
Vittoria Biotherapeutics is pioneering a novel form of CAR-T therapy for T-cell lymphoma using CRISPR gene editing. Here, co-founders Nicholas Siciliano and Marco Ruella explain how their approach promises to overcome tumour resistance, while also offering hope for new ways to treat solid cancers.