Study reveals 35 genes linked to chronic kidney disease
Posted: 23 November 2018 | Drug Target Review | No comments yet
A study conducted by researchers at The University of Manchester and Manchester Children’s Hospital has revealed 35 genes linked to chronic kidney disease…
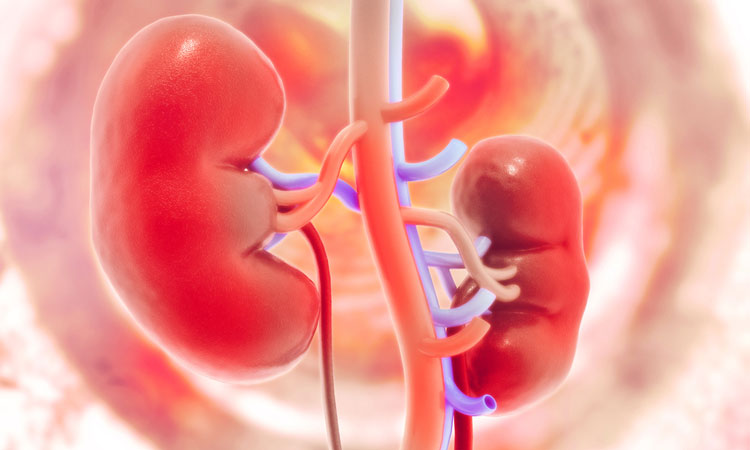

An international study lead by University of Manchester scientists has discovered the identity of genes that predispose people to chronic kidney disease.
The discovery is a major advance in understanding of the significantly under-diagnosed disorder which, if left undetected, can lead to failing kidneys that need dialysis or kidney transplantation.
The discovery of 35 kidney genes is an important step forward to the future development of new diagnostic tests and treatments for the disease that affects around one in ten adults.
Biomarkers are redefining how precision therapies are discovered, validated and delivered.
This exclusive expert-led report reveals how leading teams are using biomarker science to drive faster insights, cleaner data and more targeted treatments – from discovery to diagnostics.
Inside the report:
- How leading organisations are reshaping strategy with biomarker-led approaches
- Better tools for real-time decision-making – turning complex data into faster insights
- Global standardisation and assay sensitivity – what it takes to scale across networks
Discover how biomarker science is addressing the biggest hurdles in drug discovery, translational research and precision medicine – access your free copy today
The research teams were based in Poland, Australia and the UK.
Lead researcher Professor Maciej Tomaszewski from The University of Manchester said: “Chronic kidney disease is known for its strong genetic component.
“Our limited knowledge of its exact genetic mechanisms partly explains why progress in the development of new diagnostic tests and treatments of chronic kidney disease has been so slow.
“The findings were made possible by using a state-of-the art technology known as “next-generation RNA sequencing” applied to one of the largest ever collections of human kidneys.
“We hope that some of the kidney genes we discovered may become attractive targets for the development of future diagnostics and treatment for patients with chronic kidney disease.”
Co-author Professor Adrian Woolf from Manchester Children’s Hospital and The Universality of Manchester said: “One of the genes – mucin-1- is especially interesting.
“It makes a sticky protein called mucin that coats urinary tubes inside the kidney. Mutations of this gene have already been found in rare families with inherited kidney failure.”
Professor Fadi Charchar from Federation University Australia said: “We hope that early prediction by genetic testing even before the development of symptoms will in the future be the first line of defence against one of the world’s top killers.”
“Early detection followed by treatment using kidney-protective medication or avoidance of drugs which can damage the kidneys is the key to healthier kidneys later in life.”
Director of research operations at Kidney Research UK, Elaine Davies said: “Nearly 2 million people in the UK have been diagnosed with moderate-severe CKD by their GP but it is estimated that a further one million people remain undiagnosed. We refer to CKD as a silent killer because it is common for it to have little or no symptoms until the consequences of the disease have taken hold.
“The findings of this research are hugely important as they bring us a step closer to being able to understand, diagnose earlier and prevent kidney disease.”
The team published the Kidney Research UK funded study in Nature Communications.
Related topics
Disease Research, Drug Discovery, Drug Targets, Research & Development, Therapeutics
Related conditions
Chronic kidney disease
Related organisations
Manchester Children's Hospital, The University of Manchester
Related people
Professor Adrian Woolf, Professor Maciej Tomaszewski