$250K grant fuels development of new type 1 diabetes therapy
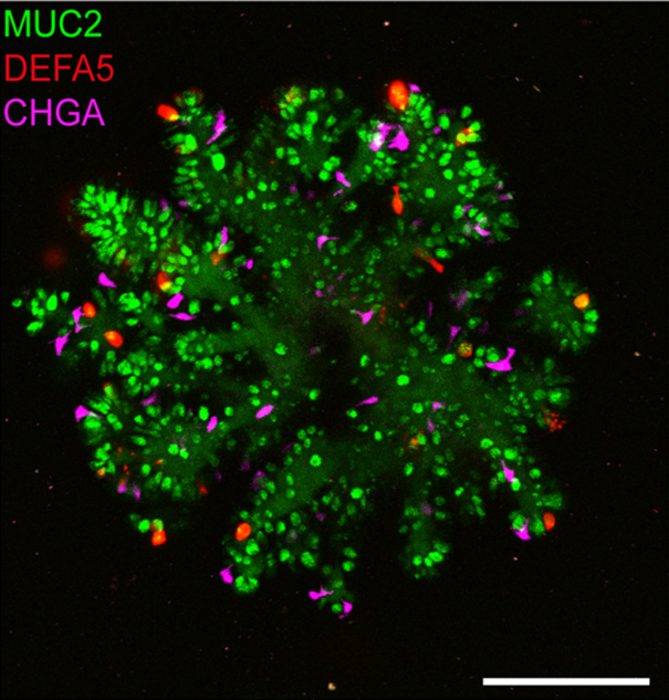
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have received a $250,000 grant from the Critical Path Institute’s Translational Therapeutics Accelerator (TRxA) to develop a novel CD22 bidentate therapeutic for type 1 diabetes to support formulation and new preclinical studies.