Researchers develop a potential tool for efficacious targeted cancer therapy
Posted: 8 October 2018 | Drug Target Review | No comments yet
Researchers have developed PeptiENV, a cancer vaccine platform, which can be used to improve the therapeutic efficacy of oncolytic enveloped viruses…

Researchers at the Faculty of Pharmacy have developed PeptiENV, a cancer vaccine platform, which can be used to improve the therapeutic efficacy of oncolytic enveloped viruses currently in clinical use. With the help of this new cancer vaccine platform, the activation of the human immune response against cancer cells becomes significantly more effective.
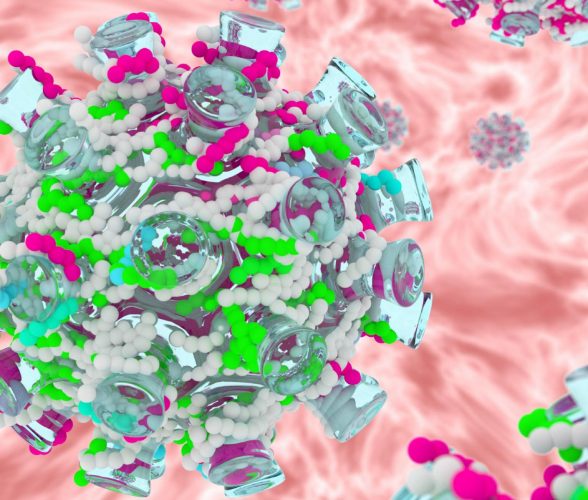

This is a cancer vaccine platform, which consists of silver-coloured enveloped viruses, onto which a patient’s cancer peptides has been tied to (in white, green and pink). CREDIT – Vincenzo Cerullo
“What is actually the most remarkable insight concerning the PeptiENV cancer vaccine platform is that we are able to envelop oncolytic viruses with the patient’s own cancer peptides, enabling tailored targeted treatment,” says Erkko Ylösmäki, an Academy of Finland post-doctoral researcher working in the ImmunoViroTherapy Lab of the Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Helsinki.
Oncolytic viruses are naturally occurring viruses that have been modified to restrict their division into cancer cells only. Virotherapy is usually administered as an injection to the tumour or the abdominal cavity, or intravenously.
A virus enveloped with peptides through the PeptiENV platform can effectively “train” the patient’s own, locally active T cells to identify tumour cells. Thus, the amount of T cells able to identify tumour cells increases in the cancerous tissue, improving the efficacy of the cancer therapy.
The study demonstrated the functionality of the PeptiENV cancer vaccine platform in conjunction with oncolytic enveloped herpes simplex virus 1, already used in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Oncolytic vaccinia viruses, among others currently under investigation in clinical trials, are also compatible with the cancer vaccine platform.
Additionally, the number of T cells in the cancerous tissue that are able to identify cancer cells strongly correlates with the therapeutic effect of new immune checkpoint inhibitors.
“We aim to expand the pool of patients that could potentially benefit from the unparalleled efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr Ylösmäki explains.
Related topics
Disease Research, Oncology, Vaccine
Related conditions
Cancer
Related organisations
Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Helsinki
Related people
Erkko Ylösmäki