Scientists control living cells using artificial protein switch
Posted: 24 July 2019 | Drug Target Review | No comments yet
Scientists have created the first completely artificial protein switch that can be ‘programmed’ to modify gene expression.
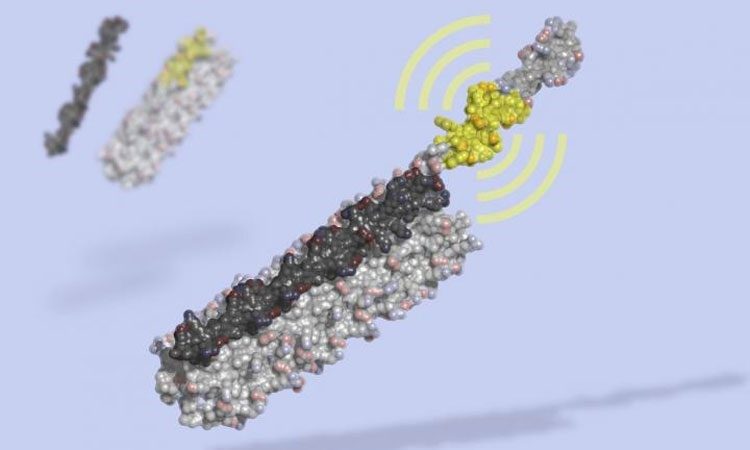

LOCKR is a molecular switch made of multiple interacting parts: a 'key' (black) unlocks a 'cage' (grey), revealing a bioactive peptide (yellow) which can interact with other molecules in the cell. LOCKR, a synthetic protein complex, was computationally designed from scratch, then tested in living cells (credit: Ian Haydon, UW Medicine Institute for Protein Design).
Scientists have created the first completely artificial protein switch (dubbed LOCKR – Latching, Orthogonal Cage/Key pRotein) that can work inside living cells to modify – or even commandeer – the cell’s complex internal circuitry. According to the developers, the switch could enable a new wave of therapies for diseases as diverse as cancer, autoimmune disorders and more.
…the switch could enable a new wave of therapies for diseases as diverse as cancer, autoimmune disorders and more
The scientists show in their research reports that LOCKR can be ‘programmed’ to modify gene expression, redirect cellular traffic, degrade specific proteins, and control protein binding interactions. They have also used LOCKR to build new biological circuits that behave like autonomous sensors. These circuits detect cues from the cell’s environment and respond by making changes to the cell. Once assembled by a cell, these new switches measure just eight nanometers on their longest side.
“The ability to control cells with designer proteins ushers in a new era of biology,” said Hana El-Samad, the Kuo Family Professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics at the University of San Francisco (UCSF) and co-senior author of the reports. “In the same way that integrated circuits enabled the explosion of the computer chip industry, these versatile and dynamic biological switches could soon unlock precise control over the behaviour of living cells and ultimately, our health.”
Biomarkers aren’t just supporting drug discovery – they’re driving it
FREE market report
From smarter trials to faster insights, this report unpacks the science, strategy and real-world impact behind the next generation of precision therapies.
What you’ll unlock:
- How biomarkers are guiding dose selection and early efficacy decisions in complex trials
- Why multi-omics, liquid biopsy and digital tools are redefining the discovery process
- What makes lab data regulatory-ready and why alignment matters from day one
Explore how biomarkers are shaping early drug development
Access the full report – it’s free!
“Right now, every cell is responding to its environment,” added one of the lead authors of the study, Bobby Langan, from the University of Washington Medicine Institute for Protein Design. “Cells receive stimuli, then have to figure out what to do about it. They use natural systems to tune gene expression or degrade proteins, for example.”
The scientists set out to create a new way to interface with these cellular systems. They used computational protein design to create self-assembling proteins that present bioactive peptides only upon addition of specific molecular “keys”.
With a version of LOCKR installed in yeast, the team was able to show that the genetically engineered fungus could be made to degrade a specific cellular protein at a time of their choosing. By redesigning the switch, they also demonstrated the same effect in lab-grown human cells.
The companion papers to this study were published in the journal Nature.
Related topics
Drug Targets, Genomics, Protein, Protein Expression, Research & Development
Related conditions
Cancer
Related organisations
Nature, University of San Francisco, University of Washington Medicine Institute for Protein Design
Related people
Bobby Langan, Hana El-Samad