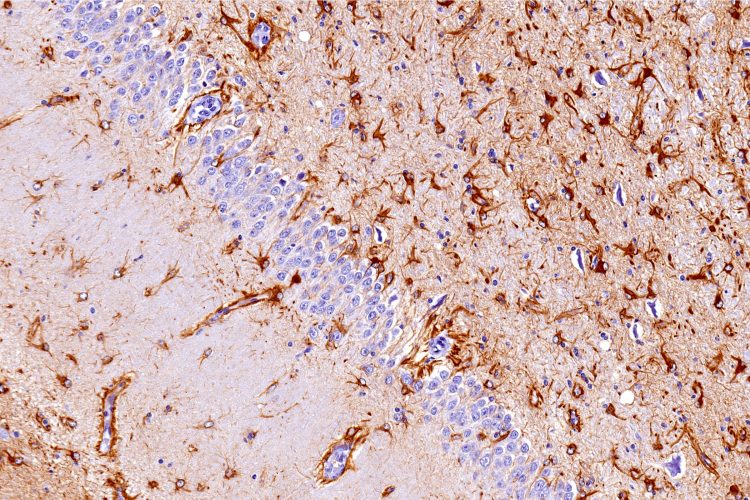
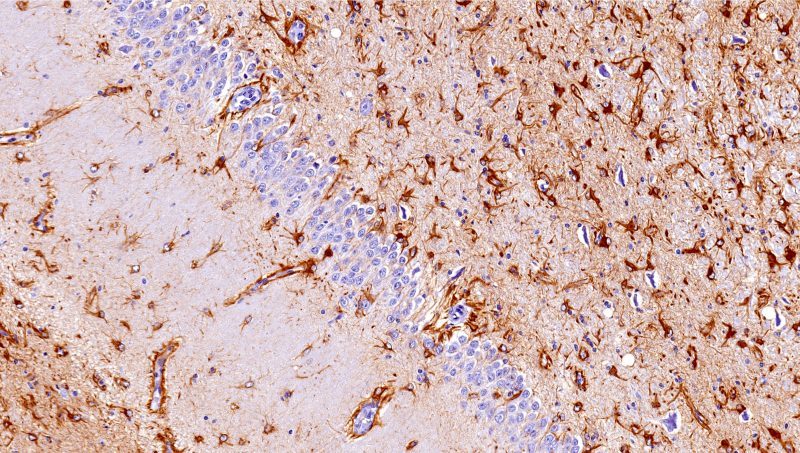
GFAP gene mutation creates tangles in brain cells – cause of neurological disease
A recent study in the U.S. has identified how a mutation in the GFAP gene, which encodes for the GFAP protein, causes the tangles in brain cells associated with Alexander disease and may also impact other neurological diseases.