Organ-on-an-electronic-chip could be used in drug development
Posted: 23 August 2019 | Victoria Rees (Drug Target Review) | No comments yet
Researchers have created a new organoid model that can be used to study systems such as the heart and the effects of drugs on these cells.

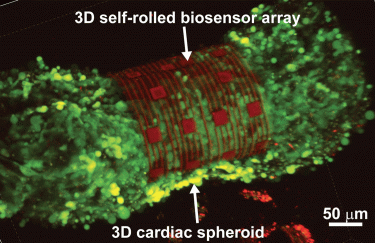

A 3D self-rolled biosensor array gripping a 3D cardiac spheroid (credit: Carnegie Mellon University).
Researchers have developed a new organ-on-an-electronic-chip platform which uses bioelectrical sensors to measure the electrophysiology of the heart cells in three dimensions. This novel model allows the researchers to study how cells communicate with each other in multicellular systems like the heart and test drug efficacy on tissues.
The team, from Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), US, and Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore, created 3D, self-rolling biosensor arrays to coil up over heart cell spheroid tissues.
“We are trying to circumvent the challenge of reading the heart’s electrical patterns in 3D by developing a way to shrink-wrap sensors around heart cells and extracting electrophysiological information from this tissue,” says Associate Professor Tzahi Cohen-Karni.
The “organ-on-e-chip” platform starts out as a small, flat rectangle, but when a bottom layer is removed, a biosensor array pinned to the tissue is released and coils up.
“Essentially, we have created 3D self-rolling biosensor arrays for exploring the electrophysiology of induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes,” says lead author of the study Anna Kalmykov. “This platform could be used to do research into cardiac tissue regeneration and maturation that potentially can be used to treat damaged tissue after a heart attack, for example, or developing new drugs to treat disease.”
The research was published in Science Advances.
Related topics
Drug Targets, Organ-on-a-Chip, Organoids, Research & Development, Screening
Related organisations
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Science Advances
Related people
Anna Kalmykov, Associate Professor Tzahi Cohen-Karni