COVID-19 In-Depth Focus 2020
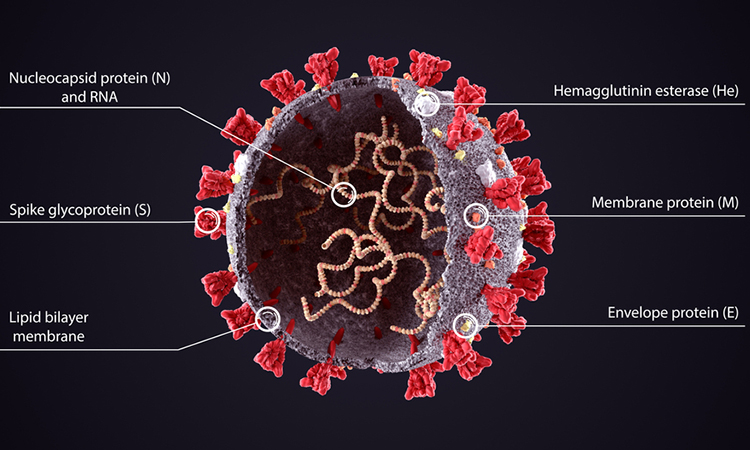
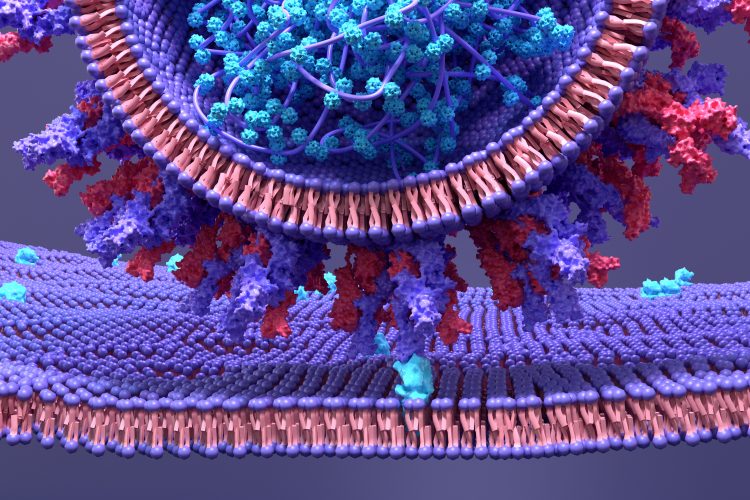
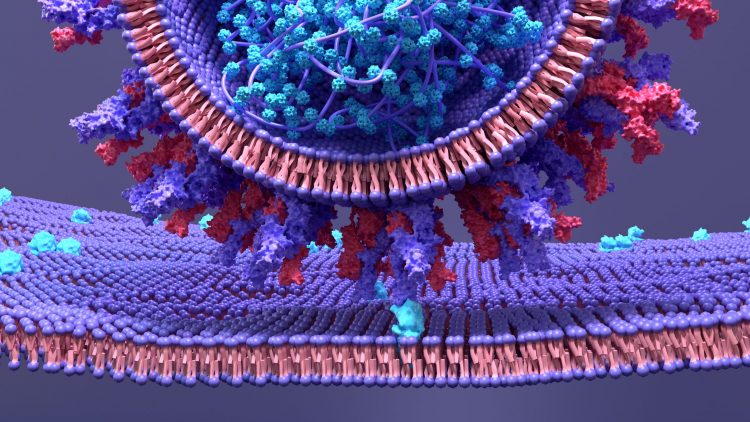
This in-depth focus features articles on neuropilin-1, a potential new target for COVID-19 drug development, the creation of a lung model to enhance our understanding of SARS-CoV-2 infections and using proteomics to uncover the mechanisms behind COVID-19 symptom severity.