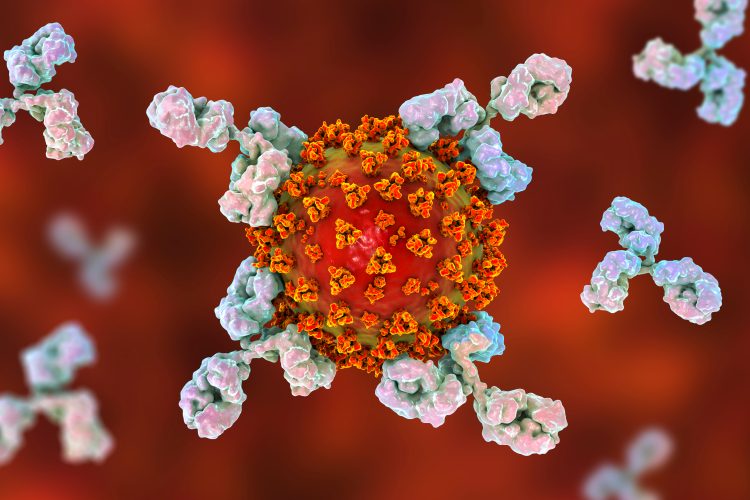
COVID-19 vaccine candidate stimulates neutralising antibody production in vivo
The novel haptenised SARS-CoV-2 s-Spike vaccine, BVX-0320, stimulated mice to create neutralising antibodies that were able to reduce SARS-CoV-2 plaques in a neutralisation test.





![A microscopy image of Leptospira bacteria [Credit: Wunder et al. (CC BY 4.0)].](https://www.drugtargetreview.com/wp-content/uploads/Leptospira-bacteria.jpg)