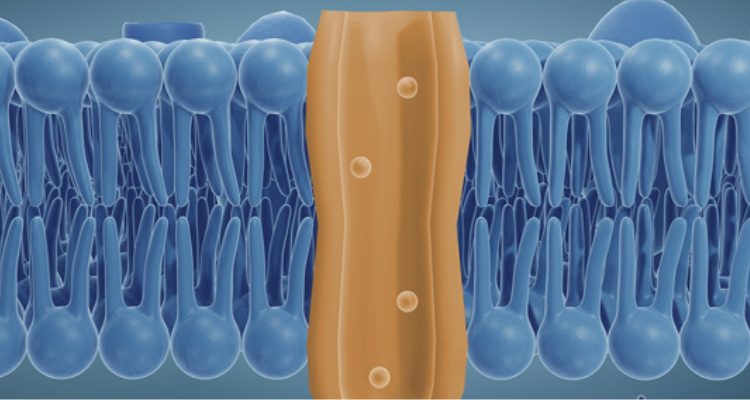
Pain Research: WRPRFa as a Novel Tool for Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3 (ASIC3)
3 September 2025 | By Eurofins DiscoverX
Join this webinar to learn how WRPRFa, a novel peptide tool selective for ASIC3, advances pain research and supports drug discovery in peripheral nociceptors.