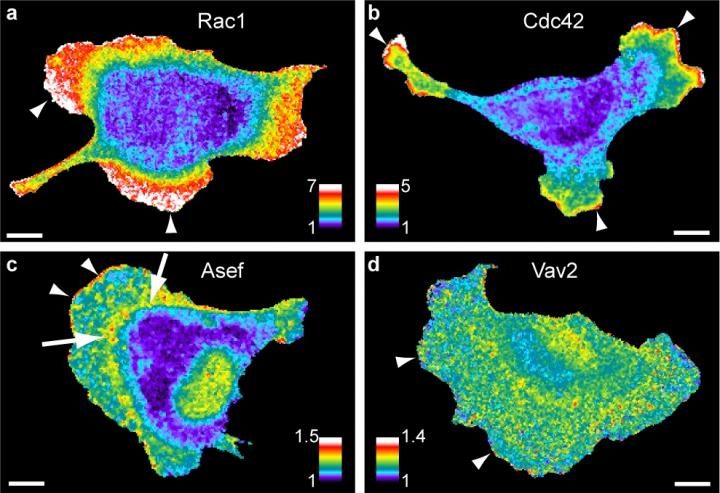
Imaging In-Depth Focus 2020
The articles in this in-depth focus discuss the difficulties in deciding what information to capture when imaging three-dimensional (3D) cell models and the use of non-invasive imaging techniques to discover small molecule drugs to control protein translation.