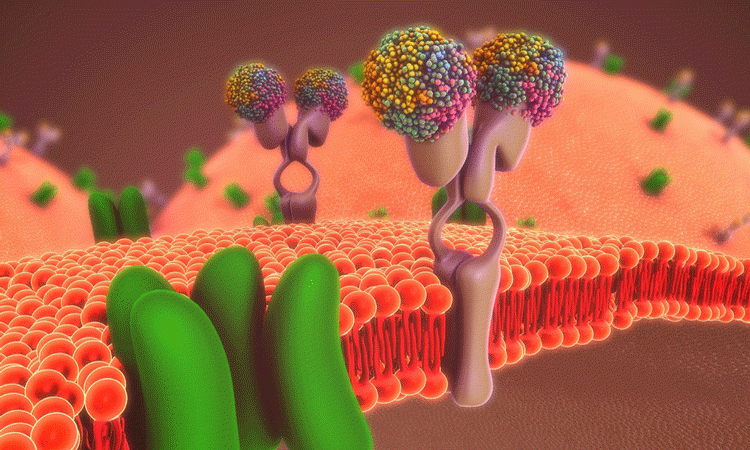
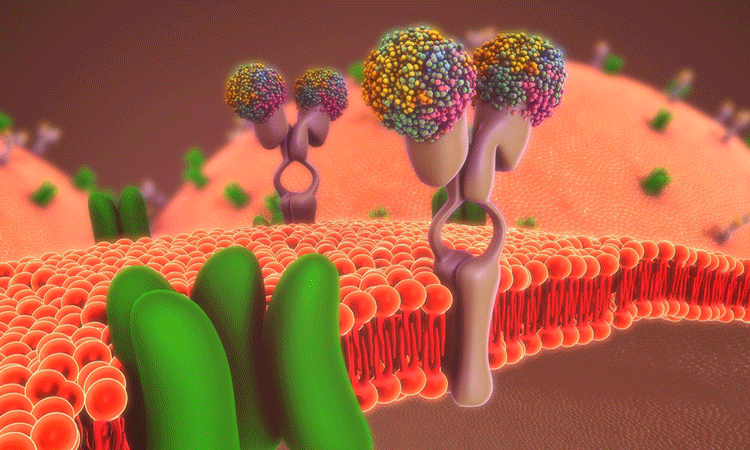
Drug Target Review – Issue 3 2019
This issue includes an investigation into utilising recombinant antibodies for research, a highlight on protein design using computational methods and an examination of the advances in genomic medicine. Also in the issue are articles on next generation sequencing and upstream bioprocessing.