List view / Grid view
Antibodies
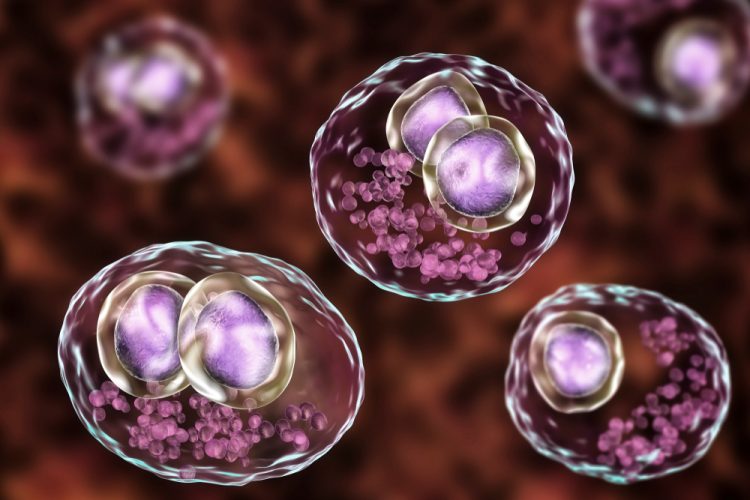
Allergy-driving cells identified as potential drug targets
Researchers have discovered a subtype of immune cells that contribute to allergic reactions and anaphylaxis, providing a drug target.
OX40-expressing follicular helper T cells can control rheumatoid arthritis
New study shows that a subset of follicular helper T cells contributes to the hyposialylation of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis.
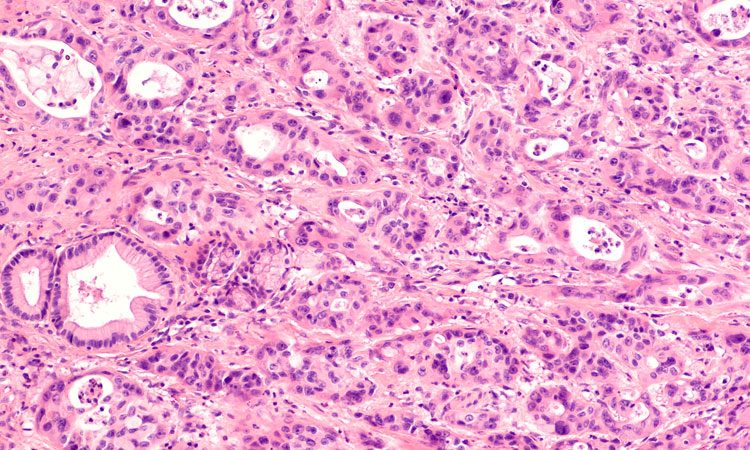
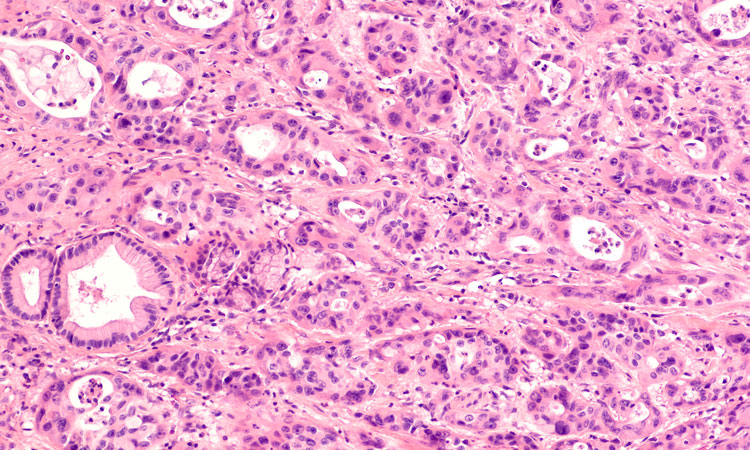
Antibody therapy extends survival in mice with pancreatic cancer
Scientists have found a way to target and knock out a protein which is widely involved in pancreatic cancer cell growth, survival and invasion.
New therapy discovered to treat acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Researchers have discovered a new combination therapy to treat drug-resistant acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, tested in pre-clinical trials.
Promising drug developed for ovarian and pancreatic cancers
An antibody has been developed to block a protein secreted by the cells surrounding ovarian and pancreatic cancer tumours.
Whitepaper: IHC/ICC Protocol Guide
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunocytochemistry (ICC) are techniques employed to localize antigen expression and are dependent on specific epitope-antibody interactions.
Whitepaper: Neural Cell Culturing Guide
The advent of in vitro culturing of neural cells has been central to driving our understanding of the nervous system.
Whitepaper: Immune Cell Isolation & Culture
Immune cell isolation and culture are necessary for both basic research aimed at investigating the functions of different immune cell types, and for expanding specific immune cell populations for therapeutic purposes.
New potential liver cancer treatment found with biomarker-guided strategy
A cellular pathway may reduce side effects and extend immunotherapy duration in patients with the most common form of liver cancer.
Role of protein in spread of cytomegalovirus discovered
A study has revealed the role of a protein which enables human cytomegalovirus to spread, the number one cause of congenital birth defects in the world.
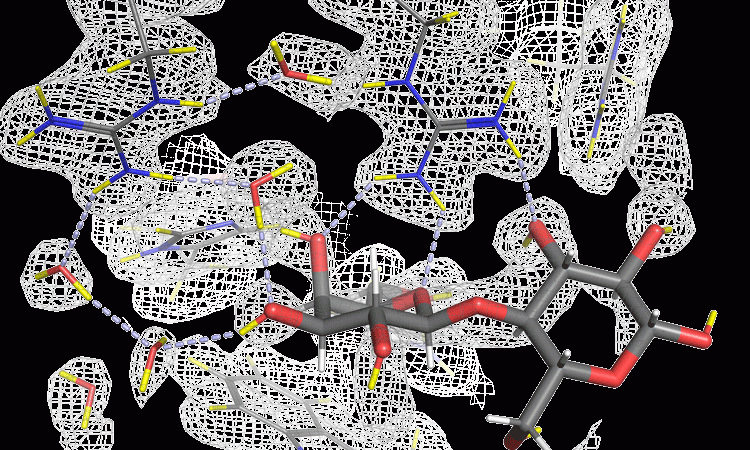
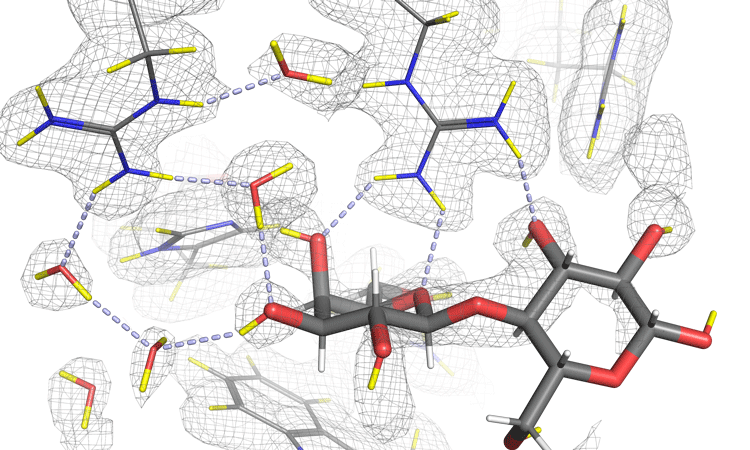
Discovering new routes to cancer drug discovery with neutrons
From the world’s flagship neutron science facility, Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL), Matthew Blakeley shares insights into how they are harnessing the power of neutrons to aid their search for new cancer treatments.
Scientists have discovered important redundancies in T cells
Redundancies have been discovered in the biochemical signalling pathways of immune cells which could impact cancer immunotherapy.
Protective antibodies identified that could be key to malaria vaccine
A new study has identified antibodies that may hold the key to creating the first effective vaccine against malaria infection in the blood.