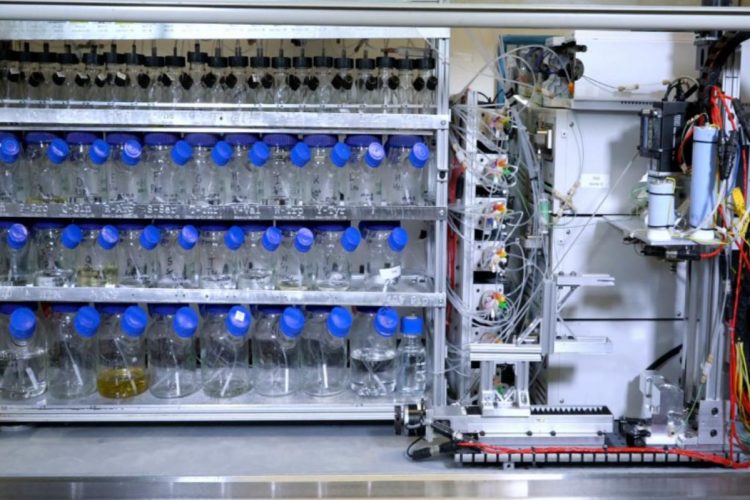
Using big data approaches to develop cell therapies
An area where stem cell biology and medicine are combining effectively is the establishment of new cell therapies. However, current therapies are limited to a narrow set of cell types that can be isolated or created and expanded in vitro. Dr Owen Rackham discusses how utilising computational approaches will further…