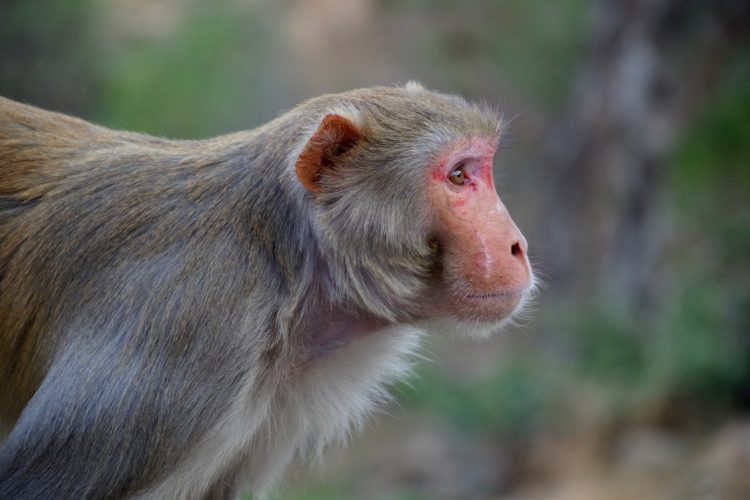
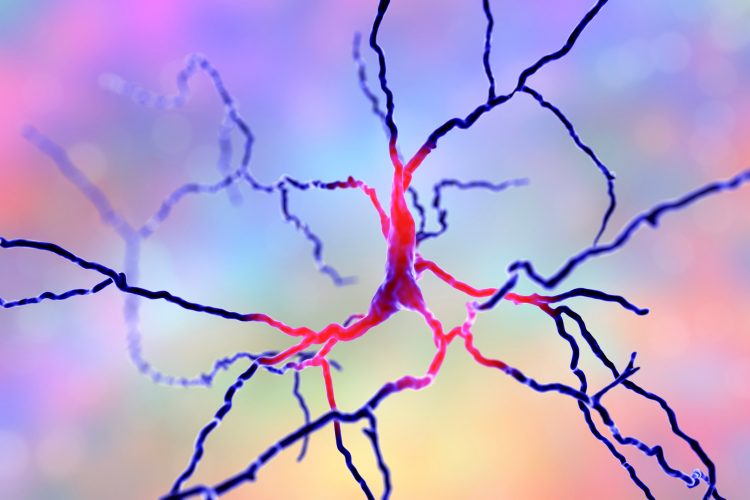
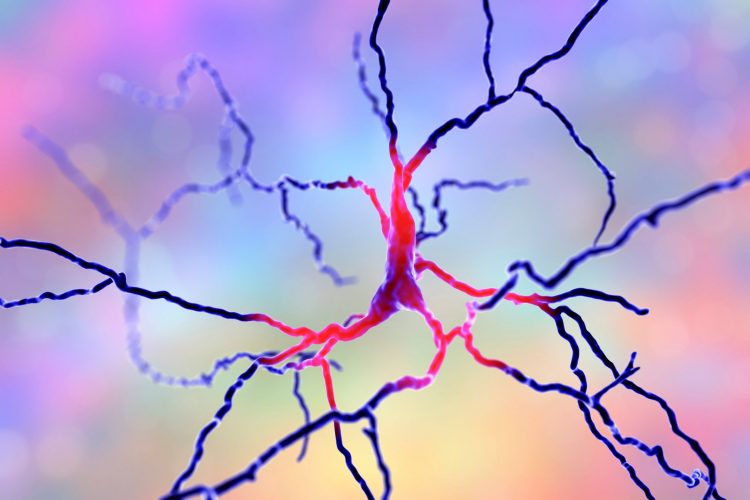
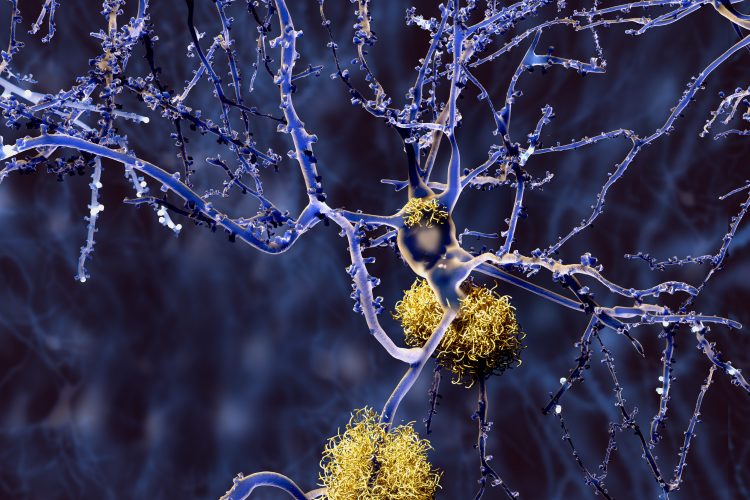
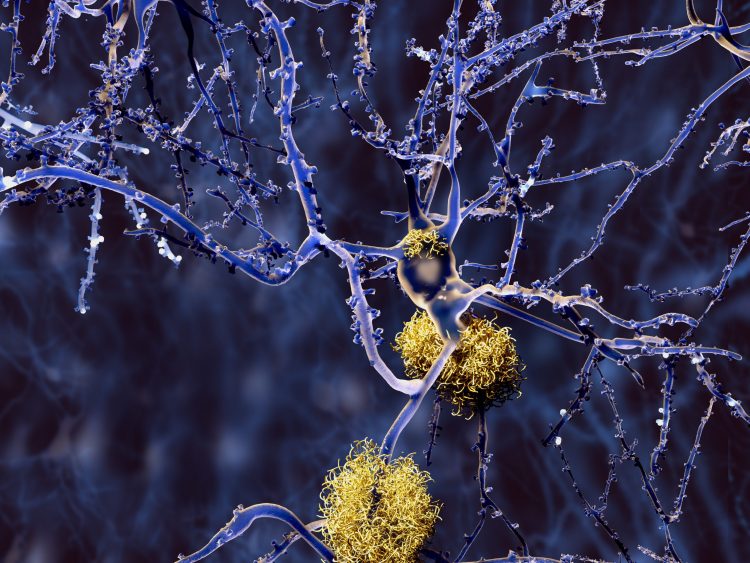
First studies of human genetic variation released by the gnomAD Consortium
The Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) Consortium has released seven papers leveraging its database to study genetic variants and their potential for guiding discovery of safer drugs.