Nafamostat inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection, preventing COVID-19 transmission
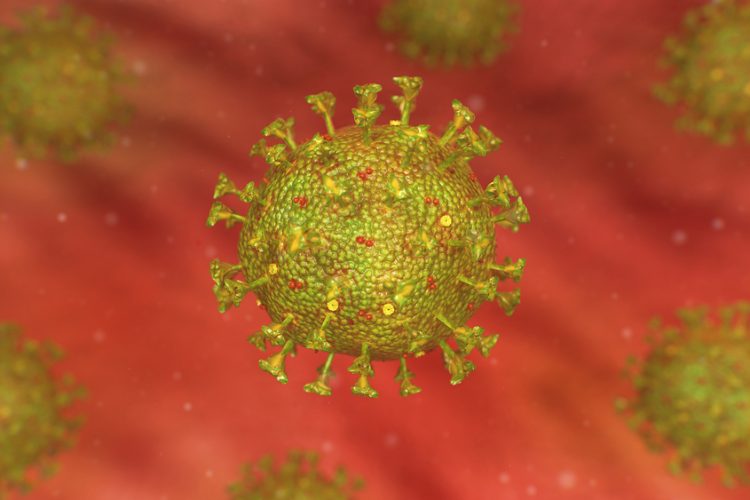
Researchers have demonstrated that Nafamostat mesylate (Fusan) can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein-initiated membrane fusion at concentrations likely achievable and safe in patients.