Targeted protein degradation: the next wave of therapeutics
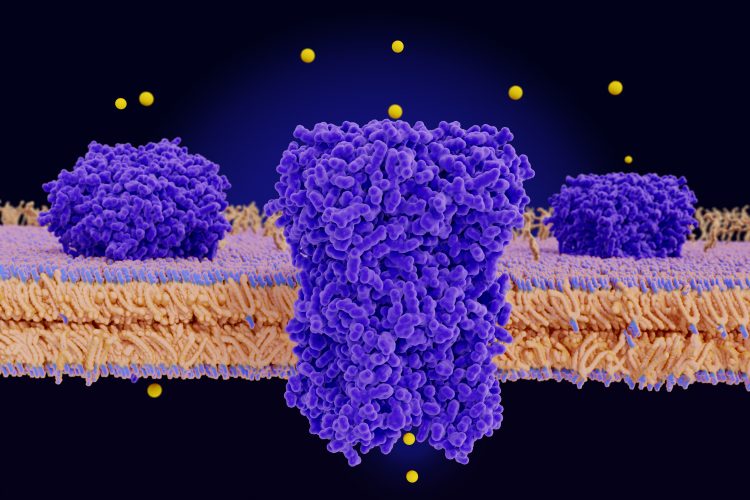
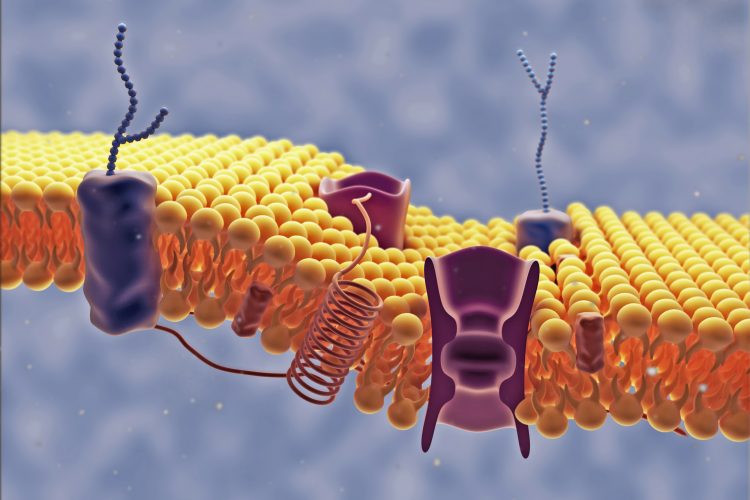
Using the ubiquitin-proteasome system to fight inflammatory conditions could provide more treatment options for patients. Dr Jared Gollob from Kymera Therapeutics explains why targeted protein degradation is the way forward for autoinflammatory and autoimmune disease therapies.