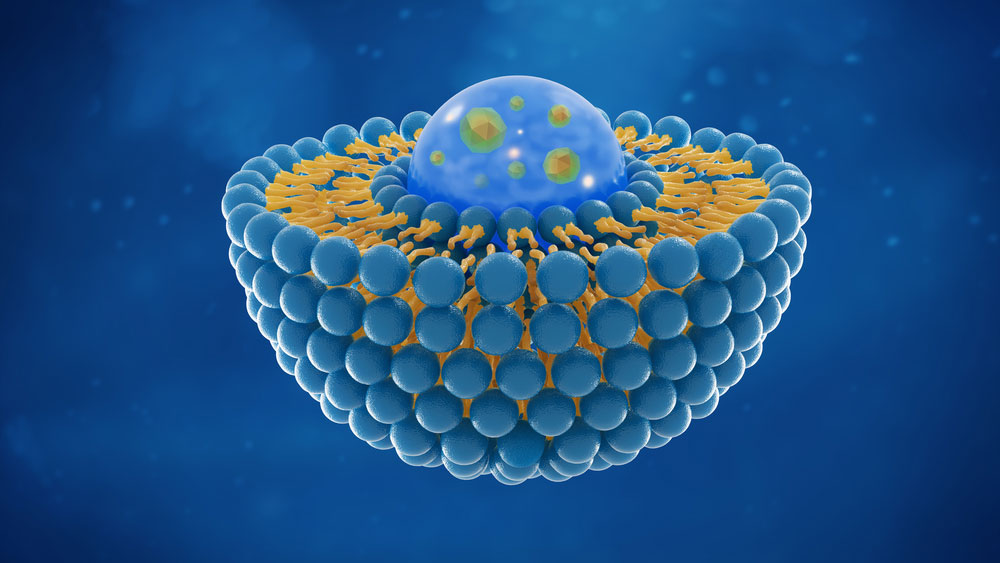
Nanoparticles could be an alternative to antibody immunotherapies
A study has shown that inexpensive nanoparticles can effectively inhibit PD-L1 in cancer cells in the lab and work as well as antibodies, providing a potential alternative immunotherapy.