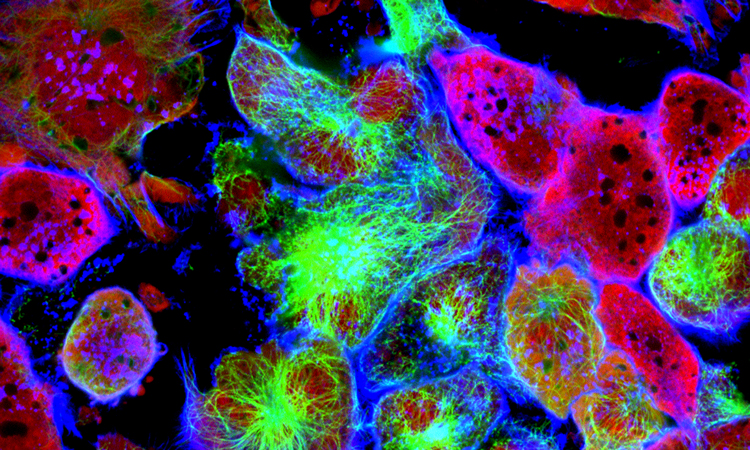
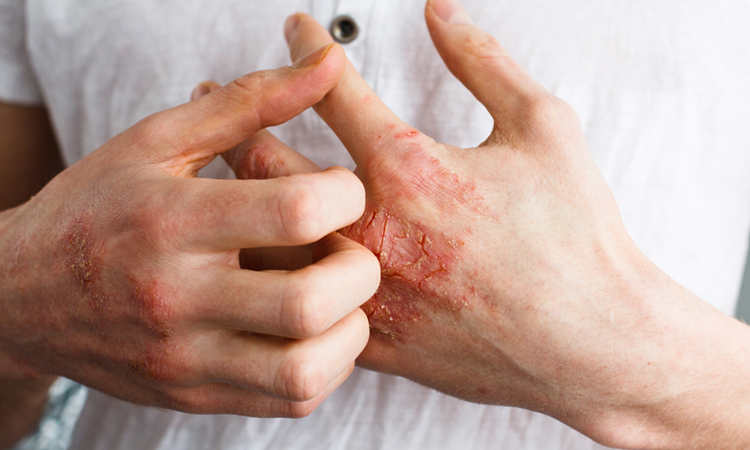
Cell division recreated in a test tube demonstrates TPX2 protein role in cancer
Studies have identified that the TPX2 protein recruits the molecular machinery required for the branching microtubule nucleation process, so could be a target for cancer therapies.