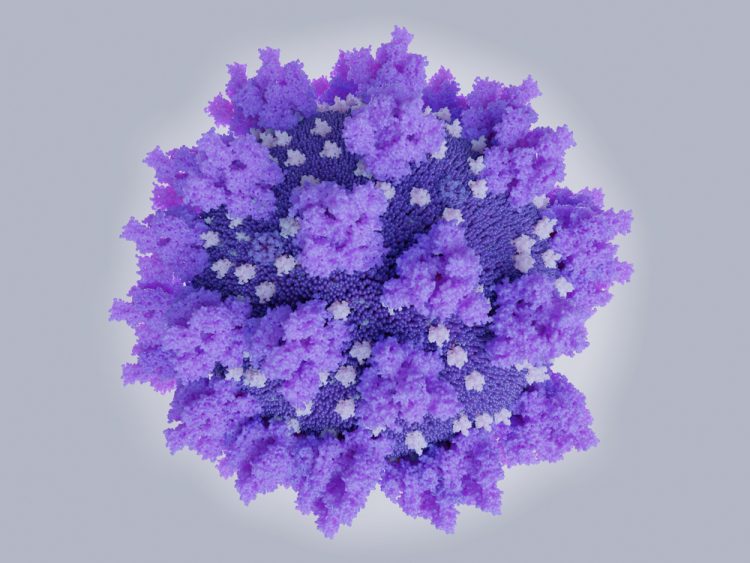
Defusing antibody neutralisers in AAV gene therapy
Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated gene therapies allow for the treatment of a growing number of diseases; however, the presence of neutralising antibodies can lead to limitations of this technology, particularly for patients who may be excluded due to these pre-existing or developing neutralising antibodies. Recently, a study was published in Nature…