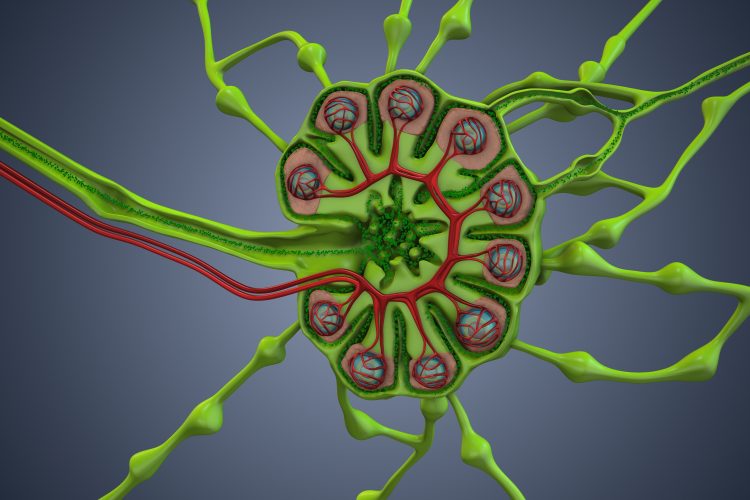
Centrifuge technique creates functional bioengineered lymph nodes
Using a straightforward cell stacking method, researchers have regenerated functional lymph nodes, offering a potential long-lasting therapy for secondary lymphedema and creating new opportunities for immunology and oncology drug discovery.